Spring Framework Architecture
This is an overview of Spring Framework Architecture. Learn how the various components of Spring Framework are organised and relates to each other. If you want to know what is Spring framework and its features please read Introduction to Spring Framework.
Overview
Spring is a modular framework. It doesn’t come as a package or bundle of multiple modules. Various spring components come as independent modules. This gives us a flexibility of use what we need and leave the rest. For example if we want to use Spring JMS module we don’t need to add the Spring Web Module to our project. This makes our application light weight and focused.
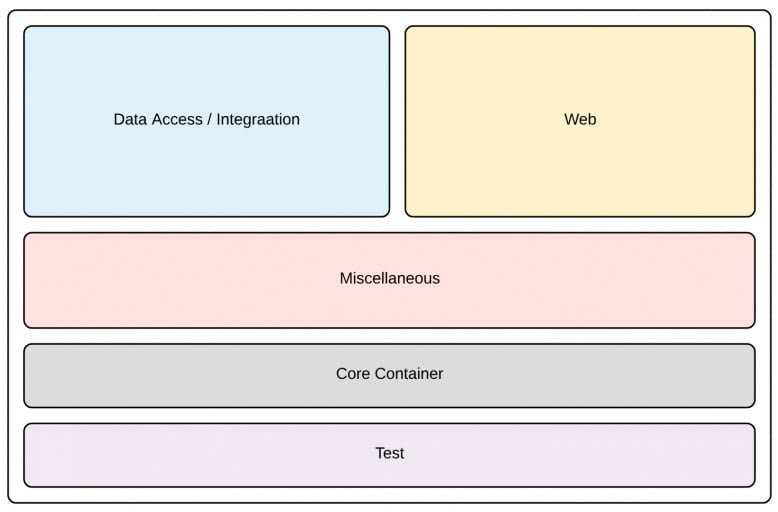
Let’s have a high level look at Spring Architecture (refer diagram) and in subsequent sections of this tutorial we will look deep in each of these modules. As shown in the diagram, the Core is a base of Spring Framework. Other modules like Web, Data Access and a miscellaneous set of modules. The test module (also based on core) stands separate as it is related to Testing the spring backed components of an application.
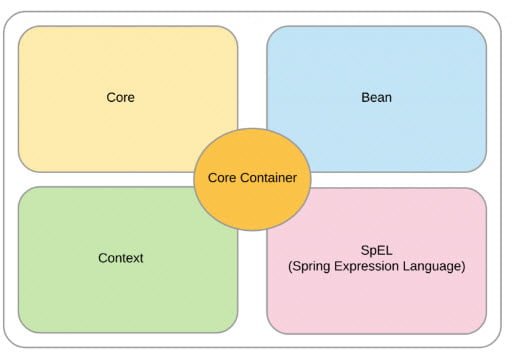
Core Container
The Core Container is heart of Spring. It contains some base framework classes and tools. The entire Spring Framework is based on top of the Core Container.
Tip:
If you are a complete newbie. The Core Container is the thing for you to get familiar first. If you understand this well, you can easily pick up any Spring Module.
Spring Core
The Core module contains basic Spring Framework classes including Dependency Injection (DI) and Inversion of Control (IOC). The Spring Core is available at Spring Core Repo. No matter which type of Spring Application you are building, you will always have direct or indirect dependency over Spring Core.
Spring Bean
Spring Bean module manages the lifecycle of beans. In the Spring Framework a Bean is any Java Class which is registered with Spring and Spring manages these bean classes. The Spring Bean module has a Bean Factory which creates bean instances, resolves bean to bean dependencies, and auto-wires the beans based on the name, or type.
Spring Bean module can be found on the Spring Beans Repo.
Spring ContextS
We learnt that Spring Bean are responsible for managing the Spring Beans. These Spring Beans are defined in the context called as a Context. In Spring every objet is a Bean, let it be a config entry or a user defined class (For example Employee). All such beans, their constructors or factory methods and dependencies are defined in the Context. The beans are accessed via Context.
Most of the time the Spring Context is started when a Spring Application starts and hence called as Application Context. Link to Spring Context Repo.
SpEL
The SpEL stands for Spring Expression Language, it a power full expression language. It is used to resolve expressions to values at runtime. SpEL can query objects graphs on runtime and can be used in XML or annotation based Bean Definition and Bean Configuration. The word runtime is really important here, as the expressions can be evaluated based on runtime configuration or values of other expressions.
Can be found at Spring Expression Language Repo.
Spring Web
As it is quite obvious from the name it self, the Spring Web components are used to build web applications. Using the Spring Web module we can build complete MVC applications, interceptors, Web Services, Portlets.
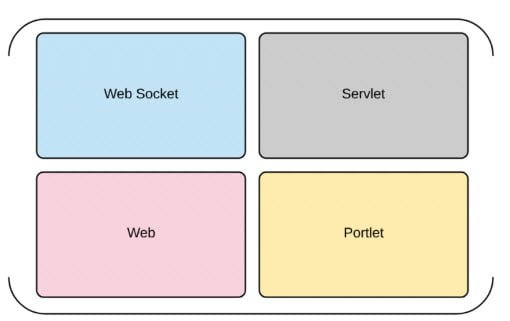
Let’s have a brief look at the web components.
Spring Web & Servlet
Spring Web and Servlets provides many features for building web integrations. We saw what is an Application Context in one of the sections above. Spring Web provides a Web Application Context which is similar to the context. Spring Web provides an abstraction for servlets and also Inversion of Control (IOC).
Can be found at Spring Web Repo.
There is one more component of Spring Web and that is Spring MVC. Spring MVC provides a mechanism for building Model View Controller based web applications. Spring MVC has a concept of View and Actions. Views represents the User Interface or a consumer and Action is the component that serves web request.
Can be found at Spring Web MVC Repo.
Spring Web Sockets
Spring Web Sockets provides support for building Web Sockets. Web Sockets are a sort of tunnel between a service and a consumer in web applications. In the HTTP connections the client has to poll on the server for any updates. With Web Sockets there is a bidirectional communication socket between both of them so that even servers can push messages to clients directly.
Can be found at Spring Web Sockets Repo.
Spring Web Portlets
Spring Web Portlets supports building web poerlets. Portlets are pluggable user interface software components that are managed and displayed in a web portal. In other words it is a mechanism to show User Interfaces of multiple applications (portlets) on a single User Interface. Usually these portlets are pluggable and arrangeable.
Can be found at Spring Web Portlet Repo.
Spring Data Access
The Spring Data Access is a set of modules, for accessing data in various formats including Database, Messaging, and XML. Let’s have a brief overview of the modules
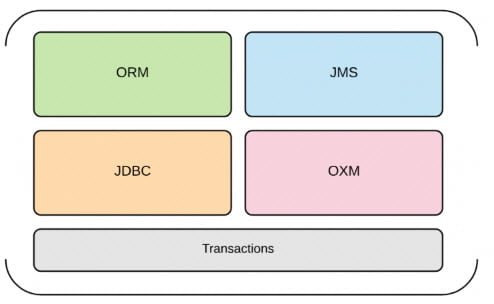
Spring JDBC
The Spring JDBC provides abstraction over Java JDBC API. When we need to access data from databases we usually need to deal with Statements, Queries, ResultSets and especially exceptions. Spring JDBC abstraction, removes all this complexity and provides JdbcTemplate to easily access data. It also provide ways of iterating and mapping the result sets.
Can be found at Spring JDBC Repo.
Spring ORM
Spring ORM provides support for integrating with various ORM implementations. ORM stands for Object Relational Mapping frameworks where data is mapped to a Java Object field by field. With ORM frameworks a plain Java object can be populated with data and passed to the ORM API to store and similarly retrieve the data in form of plain Java objects. Spring provides support for popular ORM frameworks like Hibernate, JDO, and also JPA.
Cab be found at Spring Object/Relational Mapping Repo.
Spring JMS
The JMS stands for Java Messaging Service, which defines specification for Publisher and Subscriber communication in the form of messages. Spring JMS provides an abstraction over various JMS implementations like ActiveMQ and RabbitMQ.
Can be found at Spring JMS Repo.
Spring OXM
Spring OXM provides abstraction over Java OXM implementations. The Java OXM (Object XML Marshalling) specification defines way of transferring and accessing data in the form of XML. There are various implementations of OXM like JAXB and XStream.
Cab be found at Spring Object/XML Marshalling Repo.
Spring Transactions
Spring Transactions Management API provides uniform way of managing transactions of data objets as well as databases. The Transaction API is support both programmatic as well as declarative transaction management.
Can be found at Spring Transaction Repo.
Miscellaneous Modules
Now we have reached to the last part of the tutorials. In this section we will learn about Spring’s important be kind of independent modules which can be considered as Miscellaneous category.
Spring AOP
Spring AOP is an implementation of Aspect Oriented Programming. An Aspect is any secondary task which an object needs to perform. Each object is Java has a dedicated responsibility apart from this it may have to do some secondary things like logging, or exception handling. Aspect Oriented Programming provides a mechanism for taking such secondary responsibilities out of the objects and giving them to proxy objects which doubles the original objects.
Can be found at Spring AOP Repo.
Spring Aspects
We have learnt what is Aspect Oriented Programming. Spring Aspects provides a uniform way of integrating with other Aspect Oriented Programming implementations like AspecJ.
Can be found at Spring Aspects Repo.
Spring Instrumentation
The Spring Instrumentation module provides support for class instrumentation. The instrumentation is used for monitoring performance of an application. It monitors various object to diagnose application problems and log them.
Can be found at Spring Instrument Repo.
Spring Messaging
The Spring Messaging provides support for integrating with messaging systems. The module provides simplified and uniform way of interacting with various messaging services.
Can be found at Spring Messaging Repo.
Summary
In this article we leant about Spring Framework Architecture. Spring is a huge framework having multiple module. The Core Container is back bone of everything in Spring and all other modules are dependent of Core. Along with core we have also had look at Spring Web, Spring Data Access and few miscellaneous modules.
In the upcoming sections we will continue exploring Spring Framework. Stay tuned!
Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Amit Phaltankar, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: Spring Framework Architecture Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |





