Multiple Tomcat Instances on Single Machine
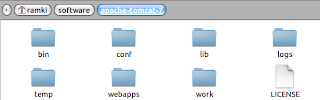
We first see the tomcat directory structure, where each folder has the following purpose:
- CATALINA_HOME
- CATALINA_BASE
- CATALINA_TMPDIR
- JRE_HOME/JAVA_HOME
- CLASSPATH
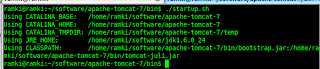
A usual way to run Tomcat is to only set the CATALINA_HOME environment variable and run the startup.sh script file. The startup.sh file automatically calculates and assigns the values of other variables which we have not set.
The startup.sh file sets the environment variable and then calls catalina.sh. This file reads CATALINA_BASE value, attaches conf i.e $CATALINA_BASE/conf folder and gets server.xml. This file is the heart of Tomcat’s configuration. It contains all configuration information, like shutdown port, connector post, host name, application folder, etc. For example, Tomcat usually uses 8080 as a connector port, so we can access it at http://localhost:8080/.
Create one folder named “tomcat-instance1” and copy conf, logs, temp, webapps, work folder from CATALINA_HOME folder and change conf/server.xml file in tomcat-instance1. We need to change these ports: shutdown port, connector port, ajp port and redirect port.
Let’s see the sample server.xml file:
<server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN"> ..... <connector connectiontimeout="20000"port="8080" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol" redirectport="8443" /> <connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectport="8443" /> </server>
So, we change these ports to different numbers, because once a port is binded, then an other process can’t bind it again. In tomcat-instance1/conf/server.xml file I configured server port =8105, connector port = 8181, ajp port = 8109.
<server port="8105" shutdown="SHUTDOWN"> ..... <connector connectiontimeout="20000" port="8181" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol" redirectport="81443" /> <connector port="8109" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectport="81443" /> </server>
Now we can create two script files for starting up and shutting down the tomcat-instance1.
startup-instance1.sh
export CATALINA_BASE= /home/ramki/tomcat-instance1 cd $CATALINA_HOME/bin ./startup.sh
shutdown-instance1.sh
export CATALINA_BASE= /home/ramki/tomcat-instance1 cd $CATALINA_HOME/bin ./shutdown.sh
Here we explicitly set the CATALINA_BASE variable and point it to the new tomcat-instance1. Then we go to the CATALINA_HOME/bin folder because all binary files for running tomcat are still present there. Then we use the startup/shutdown cripts.
Based on the above technique, we can create many instance folders and change the conf/server.xml file port values and run that instance with their own newly created script files.
Reference: Running Multiple Tomcat Instances on Single Machine from our JCG partner Rama at the Ramkitech blog (original text was modified for readability reasons).









One comment: also, if using java debugging port, you should change debugger port in different scripts.
This did not work for me, until i set $JAVA_OPTS variable to use:
-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,address=1045
in other instance instead of
-Xdebug -Xrunjdwp:transport=dt_socket,address=1044
as debugging options.
u can use CATALINA_OPTS in script file. before run the instance we need to set the CATALINA_OPTS
This is very useful. However there is no mention about where the two new script files (shutdown-instance1.sh and shutdown-instance1.sh) can go. Obviously there will not be any issue for the tomcat to start up. But if the applications are looking for files relative to working directory there could be problems. Application that works in the very first instance of tomcat, would fail in the second tomcat instance. So it is recommended to have the new script files in a folder named ‘bin’.
Check my GitHub Repo
One more thing. Please remember to remove all tomcat related applications (manager, docs, examples, default context etc) as required for your business. Some one in the team that sets up Tomcat instances for us, seems to blindly refer the steps in this blog and left out the default context :) With that the main domain points to the default tomcat page which has links to tomcat and oracle :)
Yes, thats good
good trick to make multiple instance without multiple copies of tomcat
Thanks
Hi, i tried this and almoust everything works, although when i shutdown the server, it hangs in this line: INFO: Destroying ProtocolHandler [“http-bio-8183”] and if i start it this is what i get: INFO: Initializing ProtocolHandler [“http-bio-8183”] Mar 31, 2014 4:17:01 PM org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol init SEVERE: Failed to initialize end point associated with ProtocolHandler [“http-bio-8183”] java.net.BindException: Address already in use :8183 at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.bind(JIoEndpoint.java:391) at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint.init(AbstractEndpoint.java:554) at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol.init(AbstractProtocol.java:409) at org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol.init(AbstractHttp11JsseProtocol.java:119) at org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector.initInternal(Connector.java:956) at org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase.init(LifecycleBase.java:102) at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService.initInternal(StandardService.java:559) at org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase.init(LifecycleBase.java:102) at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer.initInternal(StandardServer.java:815) at org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase.init(LifecycleBase.java:102) at org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina.load(Catalina.java:594) at org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina.load(Catalina.java:619) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:57) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:606) at org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap.load(Bootstrap.java:281) at org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap.main(Bootstrap.java:449) Caused by: java.net.BindException:… Read more »
the problem is ur using port 8183, but its already used by some process. check the netstat -tlpn command.
change the port to different one. and make sure all are unique ports (unused).
But this also happens in one instance i have with port 8181 and before this instance was working properly is this some kind of problem where there is a proccess running in this ports that weren’t shutdown and still running?
Hi,
Although my question is not directly related to the subject matter above but it is related with tomcat server. My web-app generates Matlab figures using Matlab Java Builder in the tomcat server. These figures are created at run-time and gets destroyed on server re-start. I want to know where are the these temporary files located in the server so that I can delete them with another application.
Thanks.
Very interesting
Can we run two servlets of same application in different ports using this method