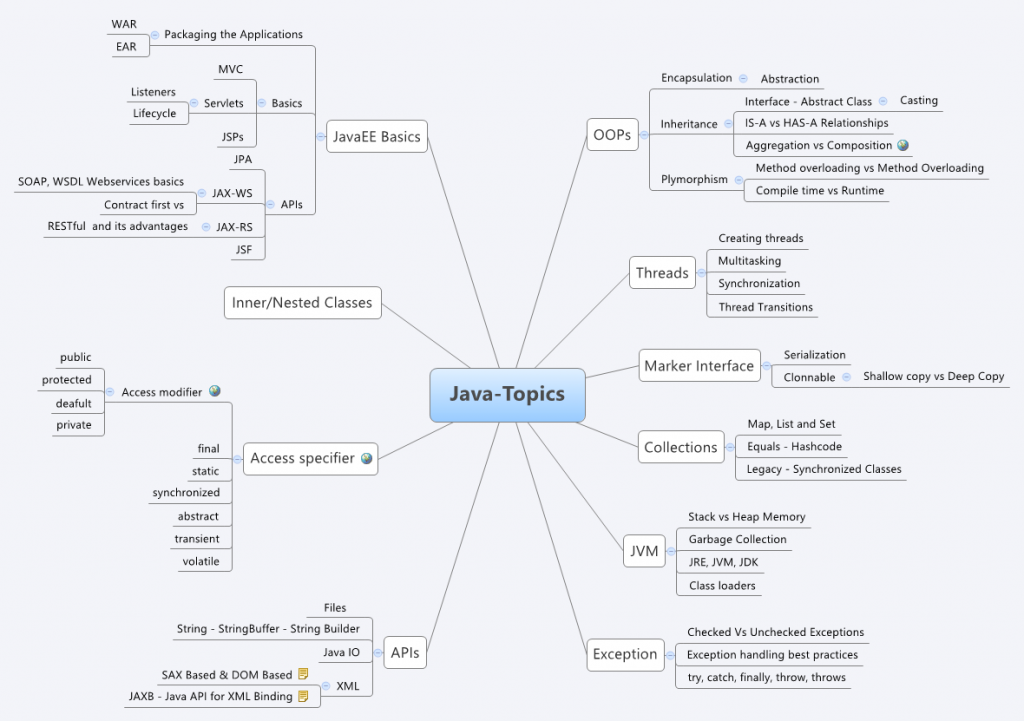
A MindMap for Java Developer Interviews
Over the years I have been a panelist in many of the interviews for Java Developers. I have previously written a post titled Top 7 tips for succeeding in a technical interview for software engineers which covers few of the general guidelines. In this post I will share a mind map containing general topics covered in a Java developer interview. I have prepared this as a general reference for myself to remember the pointers and to keep a common standard across the multiple interviews.
XMind gives a nice listing of the map. You can find the map here. Here is Image which you can download and use.
Finally here is a old fashioned tabbed content list which is easier to copy paste.
Java-Topics
OOPs
Encapsulation
Abstraction
Inheritance
Interface – Abstract Class
Casting
IS-A vs HAS-A Relationships
Aggregation vs Composition
Plymorphism
Method overloading vs Method Overloading
Compile time vs Runtime
Threads
Creating threads
Multitasking
Synchronization
Thread Transitions
Marker Interface
Serialization
Clonnable
Shallow copy vs Deep Copy
Collections
Map, List and Set
Equals – Hashcode
Legacy – Synchronized Classes
JVM
Stack vs Heap Memory
Garbage Collection
JRE, JVM, JDK
Class loaders
Exception
Checked Vs Unchecked Exceptions
Exception handling best practices
try, catch, finally, throw, throws
APIs
Files
String – StringBuffer – String Builder
Java IO
XML
SAX Based & DOM Based
JAXB – Java API for XML Binding
Access specifier
Access modifier
public
protected
deafult
private
final
static
synchronized
abstract
transient
volatile
Inner/Nested Classes
JavaEE Basics
Packaging the Applications
WAR
EAR
Basics
MVC
Servlets
Listeners
Lifecycle
JSPs
APIs
JPA
JAX-WS
SOAP, WSDL Webservices basics
Contract first vs
JAX-RS
RESTful and its advantages
JSF
This is a work in progress and I hope to refine it further. Let me know if you have any comments.



Looks good. “default” is misspelled as “deafult” though.
please correct:
Plymorphism
Method overloading vs Method Overloading
and what exactly do you expect from asking about “Aggregation” vs Composition ?
thanks for pointing out the typos. Aggregation” vs Composition is an UML concept on how you model your objects. More details can be found here – http://javapapers.com/oops/association-aggregation-composition-abstraction-generalization-realization-dependency/
jdk5 features/APIs need to be added (Generics,Concurrency API, Annotations,Enums etc.)
Other ones deserving additions: Reflection API,JNI,NIO,Networking API, JMX,Serialization,Java EE: Filters
— Correct: Cloneable instead of Clonnable
— Java I/O – Synchronous (io) Vs. Asynchronous (nio)
— The java.util.concurrent package, in particular the Atomic* classes and CAS
— Locks
What is aggregation and composition do with inheritance? They are pretty perpendicular to each other :)