Microservice Architecture – A Quick Guide
Last updated Mar. 7, 2019
1. Introduction to Microservices Architecture
Microservices is an administration arranged architecture design wherein applications are worked as a gathering of different littlest autonomous administration units. It is a product designing methodology which centers around breaking down an application into single-work modules with very much characterized interfaces. These modules can be freely conveyed and worked by little groups who claim the whole lifecycle of the administration.
The expression “small scale” alludes to the estimating of a microservice which must be sensible by a solitary improvement group ( 5 to 10 designers). In this strategy, huge applications are isolated into littlest autonomous units.
With the evolution of frontend technologies, the methodology of development is changing vastly. Today, the companies prefer to opt for an isolated Frontend and Backend project. These projects communicate with each other using services. A micro-service is the atomic form of these service APIs developed for variety of purposes. The Microservice architecture is the system design where every backend processing module is exposed to the frontend as a setup of micro-service APIs. This allows the Backend to be independent of what is going on in the frontend.
With the evolution of frontend technologies, the methodology of development is changing vastly. Today, the companies prefer to opt for an isolated Frontend and Backend project. These projects communicate with each other using services. A micro-service is the atomic form of these service APIs developed for variety of purposes. The Microservice architecture is the system design where every backend processing module is exposed to the frontend as a setup of micro-service APIs. This allows the Backend to be independent of what is going on in the frontend.
Microservice architecture provides APIs for every atomic functional task. For instance, consider a social media website. A social media website can have microservices for getting posts of a user, likes and comments for the post, user profile details and others. These services are all atomic and hence any problem in one of the service will not really affect the functioning of the system
2. Web Development Architecture History
The web development architecture has constantly evolved ever since the beginning. Earlier web application started in the form of a single server holding web resources as well as processing files like Controllers, models and business objects. The backend code was closely coupled with database and frontend in these servers. The web pages were rendered at server side in such scenarios before sending it back to the frontend. This architecture was known as monolithic architecture. There were numerous disadvantages of this architecture. They are depicted in the image below.
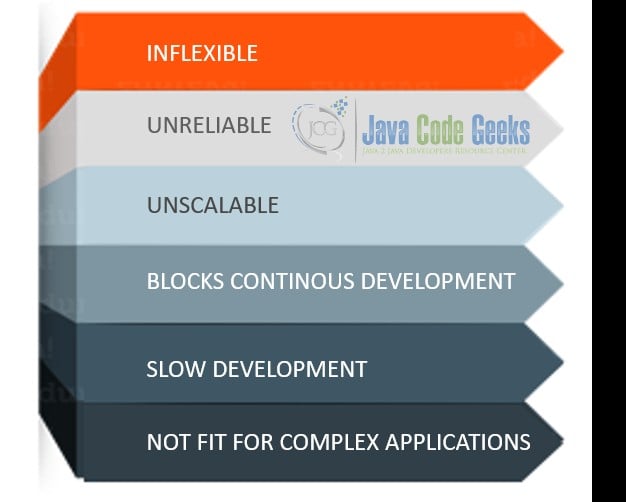
The monolithic architecture was very tightly coupled with its resources. This restricted its flexibility of implementation. Any minor break in the code logic impacted the completion web application. Due to tight coupling of frontend and backend, it already consumed a lot of hardware resources. Scaling it further would be difficult due to problems like session sharing, resource sharing and database transaction synchronisation. In a monolithic architecture, the entire code is deployed on a single server. This server is further scaled as needed. Here irrespective of the load on a specific module, the entire system needs to be scaled and upgraded whenever needed. The monolithic architecture starts getting complex when the system grows and makes it challenging to manage the entire system structure. A modularization of the code base will be a great help for the developers to reduce the possibility of breaking any other modules while coding for a specific one.
On top of this, monolithic architecture would require developers who have the knowledge of frontend as well as backend. These resources are normally costly for practical reasons. This called for the need of designing an architecture where the frontend and backend could be separated. As the frontend rendering is dependent completely on the backend development, multiple developers cannot split the work individually. This blocks continuous development process. Additionally, it also slows down the overall development process as the code start getting complex and the number of checks required to be implemented increases.
3. Evolution of Web Development Architecture
This scenario changed over the years as the ajax request came into picture. Ajax requests allowed the user to get the data without refreshing the entire page. These endpoints however sent only XML data. The AJAX requests were initially served via normal servlet endpoints. Authorising AJAX requests started getting complex as the API started increasing. There was need for a better way of implementing the requests at a common level. Another challenge in these Servlet based implemented was to managed authorisation of the calls. Since there was no common mechanism defined for managing the authorisation of the services, these endpoint started being misused by the external users. Finally, the major problem that came up was to reduce the data load to support slower networks. The normal volume of a servlet request was far more than expected. This slowed down the data calls. This made the server side rendering a better option.
This is when web services came into picture. The first type of web service that came into existence was the SOAP services. SOAP services and Ajax changed the way data exchanged. SOAP services brought in ways to strictly define data exchange standard and authorise the request for data. With SOAP services, the scenario of frontend started changing. With AJAX requests, frontend started being loosely coupled from the Backend. However, AJAX wasn’t a neat way of doing things. Managing the URLs of the ajax requests at a common level was difficult. Distributed code always leads to more error as the systems start getting complex. Moreover, tight coupling of XML message template with the response format also gave rise to need for a more flexible web service. This is when REST services came into existence.
This gave rise to frontend frameworks that defined cleaner ways to code fully REST service based web pages. Frameworks like Angular, VueJS, Backbone JS came into existence. These frameworks were backed by services that provided data as needed. They leveraged REST API calls for rendering the pages on the frontend. With this loose coupling between the frontend and backend, the entire coding pattern started undergoing transformation. The independent backend server gave the flexibility of scaling and focusing just the backend while the frontend ran on a light weight instance. However, with this feature came in the complex architectures which involved too many endpoints. This structure made it challenging to manage projects fully independent of frontend. There arose a need to allow these complex backends to be simplified.
This is how micro-service architecture came into picture. A micro-service architecture is an architecture where the backend is divided into small modules of micro-servers. These microservers provided services for specific modules of a system. For instance, consider the scenario of a banking websites. The services related to loan, insurance, banking, credit card and debit cards could be isolated into separate servers. These server can be plugged in and plugged out independently. This architecture ensures that the failure of one server does not impact the architecture of the other server.
4. Microservice Architecture – Real life example
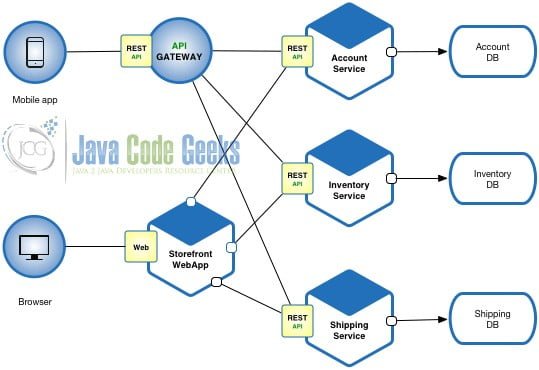
The above image excellently describes the micro-service architecture for simple shipping system. As it can be seen, the shipping system has four different modules. The Storefront, Account services, inventory services and the shipping services. All these modules are separated into independently running micro-servers. Here, it should be noted that although these servers are running independently, the API services would be accessed by a single web application or a mobile application.
Configuring a mobile application or web application to fetch data from multiple endpoints is difficult. It would make the entire architecture confusing and the system insecure as the traffic might not be directly from a single endpoint. In order to resolve this issue, we need to bring the modules to a common platform that routes the web service calls to respective micro servers. This job is done by the API Gateway.
An API gateway is a layer of proxy server or an IHS that does multiple jobs. The gateway in micro-service architecture does the below tasks:
- Route the API request to the right server based on the URL being accessed
- Block the API requests if they are coming from an unauthorised source
- Filter spam API requests that might be trying to affect the performance of servers
An API gateway can be built using many different technologies. The normal options available for building API gateway as NGINX, Apache and COMODO IHS. These are simple services that run and listen to a specific port on an independent server. This service later routes the request further based on the subdomain or the path. The gateway are pretty easy to configure and can be very helpful for primary protection of underlying micro-servers.
5. Challenges with Microservice Architecture
Microservice architecture, despite its simplicity, is a huge responsibility to handle. The more the count of servers, the greater is the responsibility of maintaining them. This section discusses the primary challenges that microservice architecture has. We will also discuss the workarounds for most of them.
5.1 Server Management
With microservices, the number of server instances that are running keep increasing. This architecture helps in maintaining lower dependency between the servers. However, at the same time, they increase the complexity in managing them. The number of components to manage increase as the number of modules increase. The modules will each add a server which would make it troublesome for the administrator. With auto-scaling in place, the system would just get worse as the server will keep increasing on its own and there would be a need for a better orchestration layer.
These problems can be solved with two major approaches. One of it is to configure CI/CD pipeline that ensures that the complete module is auto-tested and deployed across instances without any need to configure it. This will reduce the work overload of server management to a great extent. This approach would demand use of test driven development (TDD). This involves development of test to ensure that the deployment is done only when the code passes those set of steps. Skipping a test in this automated deployment system could get risky and cripple the system.
The other approach towards solving this problem is to setup an auto-scaling orchestration on systems like AWS Elastic beanstalk with AWS Codestar. These systems help you in automating not only the code build and deployment process but also help you in building application that autoscale themselves based on desired parameters.
5.2 Routing management
With increasing number of servers, the routing of the servers need to be managed well. This makes it necessary to follow the right conventions, nomenclatures and relative URLs. The route management for multiple servers might make it tricky when it comes to load balancing. We need to ensure that the right instance is routed with the respective URLs. Additionally, the firewall protection also needs to be implemented at a common layer to ensure that the proxy layer is not compromised.
5.3 Internal communication between microservices
In a monolithic architecture, communicating between different APIs and services is pretty simple as the code is on a single base. With microservices, any dependent operations will start getting complicated. In a microservice architecture, the communication between servers needs to be orchestrated using messaging queues. These queues can get complex at times when the interdependency is more. Thus, the microservice architecture should be utilised carefully if the system has more internal dependency. This issue can be normally overcome by grouping the modules right. A proper grouping to reduce the internal communication will help smoothen the system.
6. Microservice architecture – Scaling
Microservice architecture involves two different types of scaling. This section discusses these scaling types in detail here.
6.1 X-Scaling or Horizontal Scaling
This type of scaling involving scaling of the controllers across the cores available. The architecture involves provisioning of higher compute power and scaling complete system as needed. This is quite simple and involves more resources. The system is based on collective monitoring of systems.
In a horizontal scaling architecture, the systems components are divided into sub parts and arranged in a horizontal architecture. This type of scaling is normally used when the system is implemented as a MVC architecture. The micro-servers act as Controllers in this horizontal arrangement.
6.2 Y-scaling
In this type of system the tree of system resources grow vertically. The system keeps adding more machines as needed for every module. In a vertical scaling architecture, every micro-service server is scaled separately. They have their individual load balancing layer to support their architecture. In addition to these, the extra routing layer helps the routing of API calls to these load balancer. Thus, the API calls passes through at least two reverse proxy servers before being served.
Y-scaling involves multiple layers which increases the complexity of resource arrangement. The failure in case of Y-scaling is difficult to track and point. There are multiple checkpoints that need to be taken care of before reaching the root cause.
7. Microservice Architecture – Communication
The most important aspect in a microservice architecture is its internal communication. The microservice architecture involves orchestration of SOA based authentication and authorisation internally. The internal communication between microservices is dependant on the following Rules & Workflow principles.
- High Cohesion: Every sub module needs to be divided into specific atomic sub modules that perform dedicated tasks. These should be divided into as small module as possible.
- Independent: Each submodule should be as independent of other as it could be. Programmatically they should not be connected at all. The only connection that can exist is mutual message queue based communication
- Business Domain Centric: The modules should be business domain wise divided rather than multi-tier modularisation.
- Testing Automation: The testing of each module should be automated to ensure that the integration testing does not fail. Additionally, testing automation
Microservices use administration disclosure which goes about as a manual for discover the course of correspondence between every one of them. Microservices at that point speak with one another by means of a stateless server for example either by HTTP Request/Message Bus. These microservices speak with one another utilizing an Application Program Interface(API). After the Microservices convey inside themselves, they send the static substance to a cloud-based capacity administration that can convey them specifically to the customers by means of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
8. Advantages of Microservice architecture
The micro-service architecture has numerous advantages when compared to normal way of doing things. These advantages lie in the way system has been structured. A poor structuring of the system could also lead to a crippled outcome. The advantages of a rightly architected micro-service system as listed below.
- Simplified independent modules of servers that make it easier to add new modules as they get developed
- Simplified API routing using API gateway
- Higher safety against code failures in any specific modules
- Allows the developers to work independently on each module
- Allows module wise deployment for the as needed.
- The auto scaling is done only for the modules that are needed
With these advantages, come a range of disadvantages as well. These are discussed in the section below
9. Disadvantages of Microservice architecture
In a monolithic architecture, the entire system is deployed to the servers at once. This allows the systems to undergo tests in an closely integrated manner. This ensures that there is no failures due to a dependent service. However, in a microservice architecture, the normal practice is to deploy and test each module separately. Hence, if a specific module is dependent on another, constant care needs to be taken for integrating and testing them before deployment is being done. This takes away the flexibility of having the modularity in development.
In a microservice architecture, keeping a track of resources would get tricky as there are increasing number of servers on regular basis. Balancing the load rightly is a challenge. Under-utilised resources must be constantly monitored and shifted to an optimum system to ensure the cost is optimised. The next challenge in queue is its authorisation.
Authorisation of APIs is a very important aspect. Normally, the API are authorised using JWT tokens in case of a microservice architecture. Unlike monolithic architecture where the authorisation layer is integrated within the single code base, in a microservice architecture, it becomes challenging if the code needs to be done in each module. Hence, it requires orchestration of a different authorisation mechanism that can manage authorisation at a common level.
10. Best use cases for Microservice architecture
Microservice architecture is an extremely useful architecture. However, it is not the best solution for all the cases. We need to choose carefully where to use microservice architecture. This section covers precise use cases where microservice architecture is the best fit.
Microservice architecture is perfect for use for system where the following conditions are met:
- The system contains independent modules that can be separated to serve a specific purpose.
- The system has specific modules which require greater scaling compared to others
- The system can be separated into a frontend and API code
- The modules are not closely coupled but require occasional internal communication
- The system is solely dependant on APIs and does not require any server side rendering of pages.
- The data stores are separate for each module and can be managed independently
12. Conclusion
Microservice architecture is a SOA based architecture that helps in simplifying the systems involving multiple modules. With Microservice architecture, the over all flexibility of scaling specific module wise resources can be increased. This architecture helps in developing system that are modular in nature and isolated in terms of frontend and backend.
This type of architecture helps in allowing the developers to work on multiple modules in parallel without causing any conflicts in code base. This allows better project collaboration and management. However, with it comes the risk of a challenging testing orchestration. These services need to be integrated and the messages queuing and communication need to be tested before proceeding towards deployment of the system. Additionally, the microservice architecture is also a greater responsibility.





Hello,
Could anyone please provide me sample example in order to starts with the micro-services ? I’m newbie to this technology and wanted to grasp it very nicely.
Regards,
Prateek
https://docs.wso2.com/display/MSF4J100/Writing+Your+First+Java+Microservice
i am newbie user and Its asking for authentication, no registration for first timers..:(