Creating Web Services and a Rest Server with JAX-RS and Jetty
Creating a WebService in Java is remarkably easy. To add it to a ServletContainer and deploy it to an embedded WebServer is only a few more lines of code.
Let’s create a simple calculator with a couple of functions as an example of a WebService. The calculator will compute the squareRoot and square of any number. It will return a simple JSON response with the name of the action, the input and the output.
Before we start this is the Gradle configuration you will need:
apply plugin: 'java'
version = '1.0'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile group: 'org.glassfish.jersey.core', name: 'jersey-server', version: '2.7'
compile group: 'org.glassfish.jersey.containers', name: 'jersey-container-servlet-core', version: '2.7'
compile group: 'org.glassfish.jersey.containers', name: 'jersey-container-jetty-http', version: '2.7'
compile group: 'org.glassfish.jersey.media', name: 'jersey-media-moxy', version: '2.7'
compile group: 'org.eclipse.jetty.aggregate', name: 'jetty-all', version: '9.3.0.M1'
testCompile group: 'junit', name: 'junit', version: '4.11'
}This is the code for the Calculator:
package example;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.Produces;
import javax.ws.rs.QueryParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.MediaType;
@Path("calculator")
public class Calculator {
@GET
@Path("squareRoot")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Result squareRoot(@QueryParam("input") double input){
Result result = new Result("Square Root");
result.setInput(input);
result.setOutput(Math.sqrt(result.getInput()));
return result;
}
@GET
@Path("square")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
public Result square(@QueryParam("input") double input){
Result result = new Result("Square");
result.setInput(input);
result.setOutput(result.getInput()*result.getInput());
return result;
}
static class Result{
double input;
double output;
String action;
public Result(){}
public Result(String action) {
this.action = action;
}
public String getAction() {
return action;
}
public void setAction(String action) {
this.action = action;
}
public double getInput() {
return input;
}
public void setInput(double input) {
this.input = input;
}
public double getOutput() {
return output;
}
public void setOutput(double output) {
this.output = output;
}
}
}
The annotations determine the type of REST action to be applied to the method @GET, @PUT etc. The @Path annotation determines the URI of the request and the @Produces annotation determines how the response will be returned. In our case we choose JSON, the conversion of which is all handled seamlessly.
In order to deploy our WebService we need a ServletContainer for which we will use Jersey and a WebServer into which we can drop the container for which we will use Jetty.
This is the code for the RestServer:
package example;
import org.eclipse.jetty.server.Server;
import org.eclipse.jetty.servlet.ServletContextHandler;
import org.eclipse.jetty.servlet.ServletHolder;
public class RestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServletContextHandler context = new ServletContextHandler(ServletContextHandler.SESSIONS);
context.setContextPath("/");
Server jettyServer = new Server(8080);
jettyServer.setHandler(context);
ServletHolder jerseyServlet = context.addServlet(
org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer.class, "/*");
jerseyServlet.setInitOrder(0);
jerseyServlet.setInitParameter(
"jersey.config.server.provider.classnames",
Calculator.class.getCanonicalName());
try {
jettyServer.start();
jettyServer.join();
} finally {
jettyServer.destroy();
}
}
}Once you have run the RestServer you will be able to test it with this URL.
- http://localhost:8080/calculator/squareRoot?input=16
A really nice way to run queries from IntelliJ is to use the inbuilt REST Client which can be found under the tools menu.
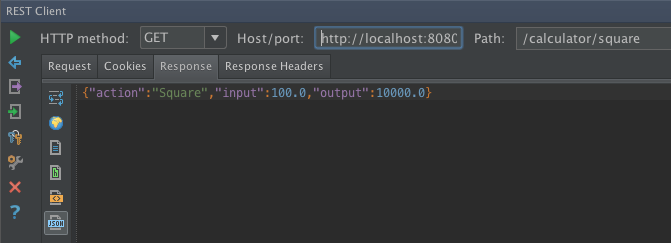
When you run the REST Client you will get this Response:
It’s a really easy way to test a RESTful server.
| Reference: | Creating Web Services and a Rest Server with JAX-RS and Jetty from our JCG partner Daniel Shaya at the Rational Java blog. |






Hi,
When i am compiling RestServer.java, its giving me error.
example/RestServer.java:21: error: cannot find symbol
Calulator.class.getCanonicalName());
How do you acesssing class name Calculator ?
Please help.
Shouldn’t “Calulator.class” be “Calculator.class”?
Thanks! Great post!
Thank you, one of the only tutorials that actually worked
Thank man for the great tutorial, works perfect on Android OS :)
Hi, good idea but when i’m need import multiple class?
Alas, not working for me:
Mar 01, 2019 9:14:14 PM org.glassfish.jersey.server.ApplicationHandler initialize
INFO: Initiating Jersey application, version Jersey: 2.7 2014-03-12 18:11:31…
2019-03-01 21:14:15.088:WARN:oejuc.AbstractLifeCycle:main: FAILED o.e.j.s.ServletContextHandler@176b3f44{/,null,STARTING}: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/xml/bind/UnmarshalException
java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: javax/xml/bind/UnmarshalException
at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods0(Native Method)
at java.base/java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredMethods(Class.java:3167)
Great Explanation, Worked for me.
there is any example that we can use a MySQL database and apply CRUD operations