Deploying Java EE Application to Docker Swarm Cluster
What is Docker Swarm?
Docker Swarm provides native clustering to Docker. Clustering using Docker Swarm 0.2.0 provide a basic introduction to Docker Swarm, and how to create a simple three node cluster. As a refresher, the key components of Docker Swarm are shown below:
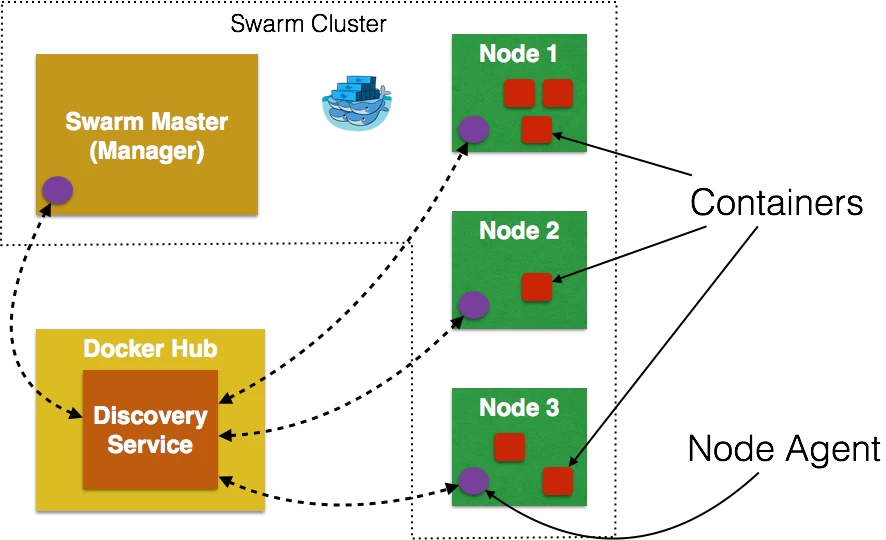
In short, Swarm Manager is a pre-defined Docker Host, and is a single point for all administration. Additional Docker hosts are identified as Nodes and communicate with the Manager using TCP. By default, Swarm uses hosted Discovery Service, based on Docker Hub, using tokens to discover nodes that are part of a cluster. Each node runs a Node Agent that registers the referenced Docker daemon, monitors it, and updates the Discovery Service with the node’s status. The containers run on a node.
That blog provide complete details, but a quick summary to create the cluster is shown below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | # Create clusterTOKEN=`docker run swarm create`# Creating Swarm masterdocker-machine create -d virtualbox --swarm --swarm-master --swarm-discovery token://$TOKEN swarm-master# Creating swarm node 01docker-machine create -d virtualbox --swarm --swarm-discovery token://$TOKEN swarm-node-01Create swarm node 02docker-machine create -d virtualbox --swarm --swarm-discovery token://$TOKEN swarm-node-02 |
Listing the cluster shows:
1 2 3 4 | NAME ACTIVE DRIVER STATE URL SWARMswarm-master virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.106:2376 swarm-master (master)swarm-node-01 virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.107:2376 swarm-masterswarm-node-02 * virtualbox Running tcp://192.168.99.108:2376 swarm-master |
It has one master and two nodes.
Deploy a Java EE application to Docker Swarm
All hosts in the cluster are accessible using a single, virtual host. Swarm serves the standard Docker API, so any tool that communicates with a single Docker host communicate can scale to multiple Docker hosts by communicating to this virtual host.
Docker Container Linking Across Multiple Hosts explains how to link containers across multiple Docker hosts. It deploys a Java EE 7 application to WildFly on one Docker host, and connects it with a MySQL container running on a different Docker host. We can deploy both of these containers using the virtual host, and they will then be deployed to the Docker Swarm cluster.
Lets get started!
MySQL on Docker Swarm
- Start the MySQL container1
docker run --name mysqldb -e MYSQL_USER=mysql -e MYSQL_PASSWORD=mysql -e MYSQL_DATABASE=sample -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=supersecret -p 3306:3306 -d mysql - Status of the container can be seen as:12
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMESb49d627a0431 mysql:latest "/entrypoint.sh mysq 5 minutes ago Up 4 minutes 192.168.99.107:3306->3306/tcpswarm-node-01/mysqldbIt shows the container is running on
swarm-node-01.Make sure you are connected to the Docker Swarm cluster using
eval $(docker-machine env --swarm swarm-master). - Find IP address of the host where this container is started:12
~> docker inspect --format'{{ .Node.Ip }}'$(dockerps-q --filter'name=*mysqldb*')192.168.99.107Note IP address of the node where MySQL server is running. This will be used when starting WildFly application server later.
ps: Filtering by name seem to not return accurate results (#10897).
WildFly on Docker Swarm
- Start WildFly application server by passing the IP address of the host and the port on which MySQL server is running:12
~> docker run --name mywildfly -e MYSQL_HOST=192.168.99.107 -e MYSQL_PORT=3306 -p 8080:8080 -d arungupta/wildfly-mysql-javaee7:hostab571708381255bfad2ff2d6b63d4c3d0659928fe8e6e9ed824e1d5e5bbcc14d - Status of the container can be seen as:1234
~> dockerpsCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMESab5717083812 arungupta/wildfly-mysql-javaee7:host "/opt/jboss/wildfly/25 minutes ago Up 25 minutes 192.168.99.108:8080->8080/tcpswarm-node-02/mywildflyb49d627a0431 mysql:latest "/entrypoint.sh mysq 34 minutes ago Up 33 minutes 192.168.99.107:3306->3306/tcpswarm-node-01/mysqldbIt shows the container is running on
swarm-node-02. IP address of the host is also shown in the PORTS column.As explained in Tech Tip #69, JDBC URL of the data source uses the specified IP address and port for connecting with the MySQL server. However passing IP address is very brittle as the MySQL server may restart on a different Docker host. This is filed as #773.
- Access the application at:12
~> curl http://192.168.99.108:8080/employees/resources/employees/<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"standalone="yes"?><collection><employee><id>1</id><name>Penny</name></employee><employee><id>2</id><name>Sheldon</name></employee><employee><id>3</id><name>Amy</name></employee><employee><id>4</id><name>Leonard</name></employee><employee><id>5</id><name>Bernadette</name></employee><employee><id>6</id><name>Raj</name></employee><employee><id>7</id><name>Howard</name></employee><employee><id>8</id><name>Priya</name></employee></collection>This is using the IP address of the host where the container is started.
Enjoy!
| Reference: | Deploying Java EE Application to Docker Swarm Cluster from our JCG partner Arun Gupta at the Miles to go 2.0 … blog. |