Top 20 Libraries and APIs Java Developer should know
One of the traits of a good and experienced Java developer is the extensive knowledge of API, including JDK and third-party libraries. I spent a good deal of time learning API, especially after reading Effective Java 3rd Edition, where Joshua Bloch has advised to use existing API for development rather than writing new pieces of code for common stuff. That advise making sense to me because of the testing exposure these 2nd party libraries get. In this article, I am going to share some of the most useful and essential libraries and API, a Java developer should be familiar with. Btw, I am not including frameworks e.g. Spring and Hibernate because they are pretty well known and have specific features.
I am generally including useful libraries for day to day stuff e.g. logging libraries like Log4j, JSON parsing libraries like Jackson, and unit testing API e.g. JUnit and Mockito. If you need to use them in your project then you can either include JARs of these libraries in your project’s classpath to start using them or you can use Maven for dependency management.
When you use Maven for dependency management, then it will automatically download these libraries, including the libraries they depend, known as the transitive dependency.
For example, if you download Spring Framework then it will also download all other JARs on which Spring is dependent e.g. Log4j etc.
You might not realize but having the right version of dependent JARs is a big headache. If you have wrong versions of the JAR then you will get ClassNotFoundException or NoClassDefFoundError, or UnsupportedClassVersionError.
20 Useful Open Source libraries for Java Programmers
Here is my collection of some of the useful third-party libraries Java developers can use in their application to do a lot of useful tasks. In order to use these libraries, Java developer should also be familiar with that and this is the whole point of this article. If you have an idea then you can research about that library and use it.
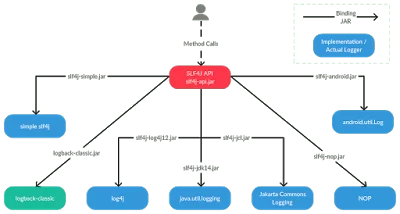
Logging libraries are very common because you need them in every project. They are the most important thing for server-side application because logs are only placed where you can see what’s going on your application. Even though JDK ships with its own logging library, there are many better alternatives are available e.g. Log4j, SLF4j, and LogBack.
A Java developer should be familiar with pros and cons of logging library and know why using SLF4j is better than plain Log4j. If you don’t know why I suggest you read my earlier article on the same subject.
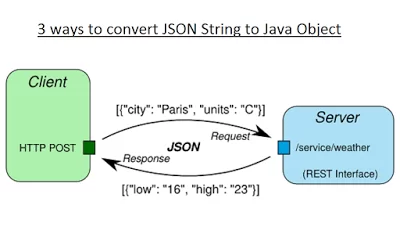
In today’s world of web services and internet of things (IoT), JSON has become the go-to protocol to carry information from client to server. They have replaced the XML as the most preferred way to transfer information in a platform-independent way. Unfortunately JDK doesn’t have a JSON library yet but fortunately, there are many good third-party libraries which allows you to both parse and create JSON messages e.g. Jackson and Gson.
A Java web developer should be familiar with at least one of these libraries. If you want to know more about Jackson and JSON, I suggest going through JSON with Java API course from Udemy, which they are offering in just $10.99 on their New Year Sale.
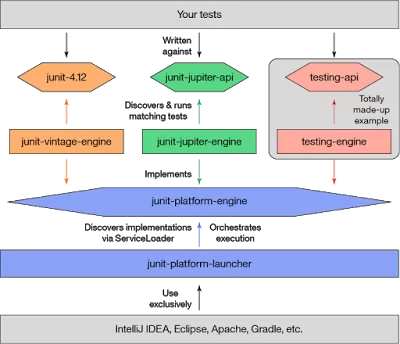
3. Unit testing libraries
Unit testing is the single most important thing which separates an average developer from a good developer. Programmers often are given excuses for not writing unit tests but the most common
excuse for avoiding unit testing is lack of experience and knowledge of popular unit testing library e.g. JUnit, Mockito, and PowerMock.
I have a goal in 2018 to improve my knowledge of unit testing and integration testing libraries e.g. JUnit 5, Cucumber, Robot framework etc.
I have also signed up for a JUnit and Mockito Crash Course in Udemy. Even if you know JUnit and basics of unit testing, you may want to refresh and upgrade your knowledge in 2018.
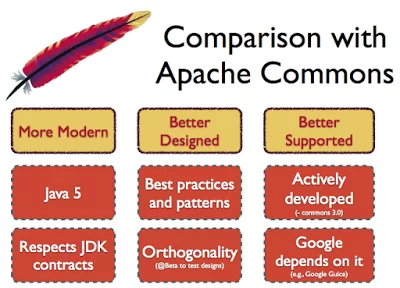
4. General purpose libraries
There is a couple of very good general purpose, third-party library available to Java developer e.g. Apache Commons and Google Guava. I always include these libraries in my projects because they simplify a lot of tasks. As Joshua Bloch has rightly said in Effective Java (now the 3rd edition is also available) that there is no point in re-inventing the wheels and we should prefer using tried and tested libraries instead of writing our own routines every now and then.
It’s just for a good Java developer to get himself familiar with Google’s Guava and Apache commons library.
5. Http libraries
One thing I don’t like much about JDK is their lack of support for HTTP. Though you can make HTTP connection using classes in java.net package it’s not as easy and seamless as by using open source, third-party libraries like Apache HttpClient and HttpCore.
Though JDK 9 is bringing the support of HTTP 2.0 and better support for HTTP, I strongly suggest all Java developers get familiar with popular HTTP client libraries e.g. HttpClient and HttpCore.
You can also check What’s New in Java 9 – Modules and More to learn more about JDK 9’s HTTP 2 support.
6. XML parsing libraries
There are many XML parsing libraries exists e.g. Xerces, JAXB, JAXP, Dom4j, Xstream etc. Xerces2 is the next generation of high performance, fully compliant XML parsers in the Apache Xerces family. This new version of Xerces introduces the Xerces Native Interface (XNI), a complete framework for building parser components and configurations that is extremely modular and easy to program.
The Apache Xerces2 parser is the reference implementation of XNI but other parser components, configurations, and parsers can be written using the Xerces Native Interface. Dom4j is another flexible XML framework for Java application. If you want to learn more about XML parsing in Java then I suggest you take a look at Java Web Services and XML online course on Udemy. It’s currently available for only $10.99 on sale.
7. Excel reading libraries
Believe it or not but all real-world application has to interact with Microsoft office in some form or other. Many application needs to provide functionality to export data in Excel and if you have to do same from your Java application then you need Apache POI API.
This is a very rich library which allows you to both read and write XLS files from Java program. You can see that link for a working example of reading Excel file in Core Java application.
8. Bytecode libraries
If you are writing framework or libraries which generate code or interact with bytecodes then you need a bytecode library. They allow you to read and modify bytecode generated by an application. Some of the popular bytecode libraries in Java world are javassist and Cglib Nodep.

The Javassist (JAVA programming ASSISTant) makes Java bytecode manipulation very simple. It is a class library for editing bytecodes in Java. ASM is another useful bytecode editing library.
9. Database connection pool libraries
If you are interacting with the database from Java application but not using database connection pool libraries then you are missing something. Since creating connections at runtime takes time and makes request processing slower, its always advised to use DB connection libraries. Some of the popular ones are Commons Pool and DBCP.
In a web application, it’s web server which generally provides these functionalities but in core Java application you need to include these connection pool libraries into your classpath to use database connection pool. If you want to learn more about JDBC and connection pool in a web application, I suggest you take a look at JSP, Servlet, and JDBC for Beginners course in Udemy.
10. Messaging libraries
Similar to logging and database connection, messaging is also a common feature of many real-world Java application. Java provides JMS, Java Messaging Service but that’s not part of JDK and you need to include separate jms.jar. Similarly, if you are using third-party messaging protocol e.g. Tibco RV then you need to use a third-party JAR like tibrv.jar in your application classpath.
11. PDF Libraries
Similar to Microsoft Excel and World, PDF is another ubiquitous format. If you need to support PDF functionality in your application e.g. exporting data in PDF files then you can use the iText and Apache FOP libraries. Both provide useful PDF related functionality but iText is richer and better and I always preferred that one. See here to learn more about iText.
12. Date and Time libraries
Before Java 8, JDK’s data and time libraries have so many flaws e.g they were not thread-safe, immutable, and error-prone and many Java developer relied on JodaTime for implementing their date and time requirement. From JDK 8, there is no reason to use Joda because you get all that functionality in the JDK 8’s new Date and Time API itself but if you are working in older Java version then JodaTime is a worth learning library.
If you want to learn more about new Date and Time API, I suggest you to please check the What’s new in Java 8 course from Pluralsight. It provides a nice overview of all important features of Java 8, including Date and Time API.
13.Collection libraries
Even though JDK has a rich collection libraries, there are are some 3rd party libraries which provide more options e.g. Apache Commons Collections, Goldman Sachs collections, Google Collections, and Trove. The Trove library is particularly useful because it provides high speed regular and primitive collections for Java.
FastUtil is another similar API, it extends the Java Collections Framework by providing type-specific maps, sets, lists and priority queues with a small memory footprint and fast access and insertion; provides also big (64-bit) arrays, sets, and lists, and fast, practical I/O classes for binary and text files.
14. Email APIs
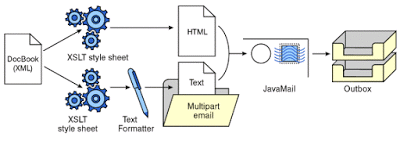
The javax.mail and Apache Commons Email – provide an API for sending an email. It is built on top of the JavaMail API, which it aims to simplify.
15. HTML Parsing libraries
Similar to JSON and XML, HMTL is another common format many of us have to deal with. Thankfully, we have jsoup which greatly simplify working with HTML in Java application. You can use JSoup to not only parse HTML but also to create HTML documents
It provides a very convenient API for extracting and manipulating data, using the best of DOM, CSS, and jquery-like methods. jsoup implements the WHATWG HTML5 specification and parses HTML to the same DOM as modern browsers do.
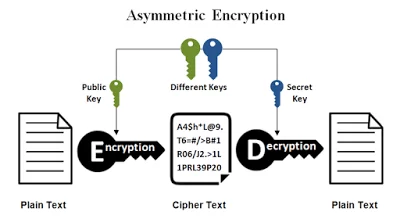
16.Cryptographic library
The Apache Commons Codec package contains simple encoder and decoders for various formats such as Base64 and Hexadecimal. In addition to these widely used encoders and decoders, the codec package also maintains a collection of phonetic encoding utilities.
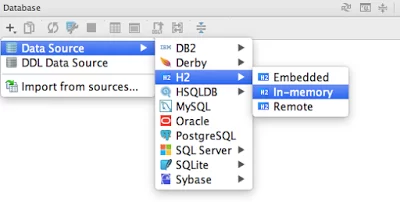
17. Embedded SQL database library
I really love in-memory database like H2, which you can embed in your Java application. They are great for testing your SQL scripts and running Unit tests which need a database. Btw, H2 is not the only DB, you also have Apache Derby and HSQL to choose from.
18. JDBC Troubleshooting libraries
There are some good JDBC Extension libraries exists which makes debugging easier e.g. P6spy. It is a library which enables database data to be seamlessly intercepted and logged with no code changes to the application. You can use these to log SQL queries and their timings. For example, if you are using PreparedStatment and CallableStatement in your code then these libraries can log an exact call with parameters and how much time it took to execute.
19. Serialization libraries
Google Protocol Buffer Protocol Buffers are a way of encoding structured data in an efficient yet extensible format. It’s richer and better alternative to Java serialization and I strongly recommend experienced Java developer to learn Google Protobuf. You can see this article to learn more about Google Protocol Buffer.
20. Networking libraries
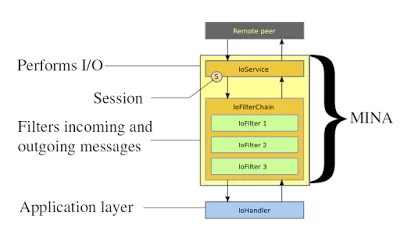
Some of the useful networking libraries are Netty and Apache MINA. If you are writing an application where you need to do low-level networking task, consider using these libraries.
That’s all about some of the useful libraries every Java developer should be familiar with. Java Ecosystem is very vast and you will find tons of libraries for doing different things. You think about something and you will find there is a library exists to do just that. As always, Google is your best friend to find useful Java libraries but you can also take a look at Maven central repository to find some of the useful libraries for your task at hand.
If you like this article, you may find my other articles useful too:
- 10 Things Java Developer Should Learn in 2018
- 10 Programming Languages to explore in 2018
- 10 Frameworks Java and Web Developers should learn in 2018
- 20 Java Books You Can Read in 2018
- 10 Ways to Learn a New Technology in 2018
- 10 PluralSight Courses for Java and Web Developers
- 10 Tutorials to Learn Java 8 Better
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this article then please share with your friends and colleagues too. If you have any feedback or questions then please drop a note.
P.S. – If you want to start 2018 in good note then I suggest you to read
Effective Java 3rd Edition, one the must read book for every developer. It’s not updated for Java 7, 8, and 9 and most of the items are updated keeping new changes in mind.
| Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Javin Paul, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: Top 20 Libraries and APIs Java Developer should know Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |






Since Java EE 8 (2017) JSON could (and should in my view) be processed by JSON-B 1.0 and JSON-P 1.1. Yasson is the reference implementation. Jackson and Gson (and others) are subsumed in this standard and contributed to it.
Haben Sie Probleme mit Ihren Genitalien, die Sie nicht lösen können? Sie sollten also unbedingt versuchen, hier erfahren Sie mehr zu gehen, denn hier kann ich immer gute Medikamente kaufen, die mir immer helfen