Functional Testing Vs Non-Functional Testing
According to a report, app crashes cause 71% of uninstalls. Others reasons that compel users to uninstall the app are page response time, confusing UI, battery consumption, etc. This indicates the importance of functional testing as well as non-functional testing to deliver a user-friendly app. So let’s understand what is functional testing.
What is Functional Testing?
Functional testing is done to make sure that the functions of an app are working in conformance with the requirement specification. It is black box testing and does not go into the details of the source code of the app. While performing functional testing the focus should be on the user-friendliness of the main functions of the app.
To perform functional testing first we need to identify test input and compute the expected outcomes with the selected test input values. Then execute the test cases and compare the actual data to the expected result.
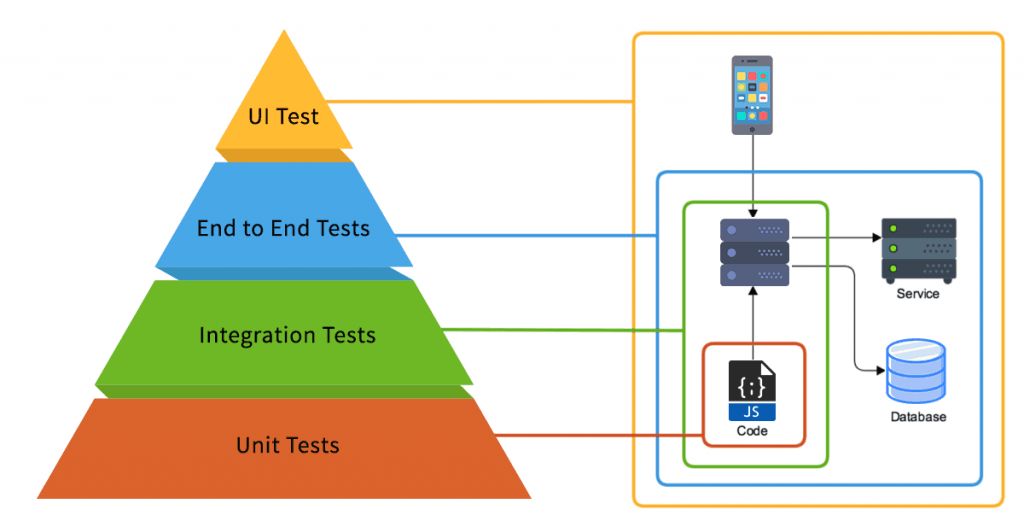
Functional Testing Types
Let’s have a look at different types of functional testing for mobile applications.
Unit Testing
In Unit Testing, individual components of a software application are tested during the development phase. Unit Testing is usually done by developers instead of testers. A function which is in the form of a section of code is tested to verify the accuracy. Drivers, unit testing frameworks, mock objects, and stubs are used to perform unit testing.
Unit testing is usually Automated, but sometimes it can be done manually. A manual approach can be done with the help of an instructional document. Unit testing can be performed on all types of mobile applications.
In automated unit testing, a developer writes code in the app to test the function or procedure. Once the app is deployed, that code can be removed. The function can be isolated to test the app rigorously and it reveals the dependencies between the code being tested and other units. Then the dependencies can be eliminated. Most of the developers use unit test automated framework to log the failing test cases.
Integration Testing
Integration testing is done to check if the individual components of the app function as expected when integrated. Integration testing is usually done after unit testing when all the builds are tested and combined.
Sanity Testing
Sanity testing is performed after receiving the software build with minor changes in the functionality to make sure that the errors are rectified and there will be no issues due to these changes in the future. The goal is to test the function on a superficial level and not thoroughly to see if the developer has rationally built the function or not.
Usually, these following steps are considered while performing sanity testing. Mark the modifications introduced in the code with the newly added features. Evaluate these marked features to ensure if they are fulfilling their motive. Then test the related features, associated parameters, and elements to ensure their proper working. After all this, the build can be subjected to other advanced testing methods. It’s better to use a cloud-based testing platform rather than online Android emulators as they provide hundreds of device browser combinations.
Smoke Testing
It is done to check if the build is stable enough to proceed with further testing. Smoke testing is done end to end and not for a particular component as we do insanity testing.
Regression Testing
Regression testing is done to check if the newly added code does not have any adverse effect on the functionality of the app. This is done when there is a new feature added in the app or simply if there are some changes in the code. The changes in the code can impact the existing flow of the product or have bugs. This can be evaluated by doing regression testing. In regression testing, the motive is to initiate the optimization, enhancement and fixing the issue if needed in the existing feature.
System Testing
System testing is the testing of a fully integrated software product. The software is interfaced with hardware and other software and a series of test are conducted on the fully integrated app on the system. It can be a white box or black box both.
Beta/User Acceptance Testing
This testing happens in the final phase of the testing process before the app is ready to be released. It is performed by the client/user to validate end to end business flow and the user-friendliness.
What is Non-Functional Testing?
Nonfunctional testing is designed to evaluate the readiness of an app with various criteria like in load testing, scalability testing, stress testing, etc. It evaluates how well the app will perform in challenging conditions.
Non Functional Testing Types
Let’s look at the 5 major types of non-functional testing for mobile applications.
Performance Testing
Performance testing is done to ensure that the app will work smoothly under the expected workload. The goal is to find the performance issues like reliability, resource usage, etc and not to find bugs. Three main things that we should keep in mind while doing performance testing are quick response, maximum user load, and stability in a varied environment. Even if you are focusing on mobile testing and using online Android emulators, performance testing cannot be avoided.
Types of Performance Testing:
Endurance Testing:
This done to check if the app can withstand the load that it is expected to have to endure for a long period of time.
Scalability Testing:
It is done to check the performance of an app in maximum load and minimum load at software, hardware, and database level.
Load Testing:
In this, the system simulates actual user load on any app to check the threshold for the max load the app can bear.
Stress Testing:
This is done to check the reliability, stability and error handling of an app under extreme load conditions.
Spike Testing:
In this, an app is tested with sudden increment and decrement in the user load. By performing spike testing, we also get to know the recovery time for the app to stabilize.
Volume Testing:
This done to analyze the apps behavior and response time when flooded with a large amount of data.
Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing is performed to make sure that the app works as expected on different hardware, operating systems, network environments, and screen sizes.
Security Testing
Security testing is the most important part of the mobile app testing process and it ensures that your app is secure and not vulnerable to any external threat like malware and virus. By doing this we can figure out the loopholes in the app which might lead to loss of data, revenue or trust in the organization.
Let’s have a look at the major security threats that should be eliminated during security testing.
Privilege elevation
In this, the hacker might app but he/she can increase the privilege that has been provided by already have an account in your app and using the services provided by your default. For example, if the app has a clause for some credits for referring this app to a friend then the hacker can extend the limit and get more money out of it.
Unauthorized data access
The most common type of attack is by gaining unauthorized access to fetch valuable information. This can be done simply by hacking the login credentials or by hacking the server to access the data.
URL manipulation
Hackers manipulate the URL query string if the app or website used HTTP GET method to transfer data between the client and the server. The QA team can pass a modified parameter value to see if the server accepts it.
Denial of service
This type of attack is done to render the services of the app by making it inaccessible to the end-users. In this, the hackers can also rapture the working mechanism of the app and the server machine to make it unstable.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is performed by a small set of users to figure out the usability defects in the application. It is done in the initial phase of software development when the design is proposed. The focus is on how easy it is for the user to use the app and if the system is meeting its expected objective. This type of mobile testing can also be performed on online android emulators.
There are a few methods by which we can carry out the usability testing. One is during the design phase where you can evaluate the design by just drawing on a piece of paper. Random tests can also be done once the app is build to check for usability. That can be done by real users on the site which can then provide the result. Apart from that, a tool might be very helpful with the statistics based on the inputs on design and wireframes.
The first step to perform usability testing structurally is to identify the user to perform the usability app. It is necessary to choose the users according to the behavior of the app with a difference in geography, age, gender, etc. The next step is to design the task that the user is supposed to perform and then it the time to analyze the results of the testing done.
Usability can be done in an isolated test area in front of observers who will inspect the testing and create a report on the assigned task. The next option is remote usability testing. In this, the observer and the testers are located in different locations and the task assigned is done remotely. Testers details like their reactions will be recorded by automated software.
Localization Testing
This is done to assure that the app is customized and behaves as per the culture of the country in which it will be available. The key focus is on the content and the UI of the app. The app goes through a process of testing to check if the default language, date & time format, currency, etc are designed as per the targeted region.
Difference between Functional Testing and Non-Functional Testing
| Functional Testing | Non-Functional Testing |
|---|---|
| It is done to validate the actions and operations of an application. | To verify the performance of the application. |
| Focus is on user requirements. | Focus in on user expectations. |
| It is executed before non-functional testing. | It is executed after functional testing. |
| It is easy to define functional requirements. | It is difficult to define requirements for non-functional testing. |
| Eg: Check login functionality. | Eg: the page should load in 1 second. |
| Functional testing is easy to be executed by manual testing | Non-functional testing should be automated. |
Conclusion
On average, an app loses 95% of the new users after the first 3 months. This is because there is less focus on the testing and as a result the app has bugs. This can be avoided with a good strategy and tools to perform functional testing and non-functional testing on the apps.
Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Balamurugan, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: Functional Testing Vs Non-Functional Testing Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |





Great post! Thank you for sharing the difference between functional and non-functional testing and this is a great post to share with software testing trainee because, this post will help them to have a look at different types of testing.