How to Convert a Java Object into a JSON String
When learning how to write Java-based software, one of the first snags developers hit is how to connect their code with other software. This is usually where JSON comes in. While you might be a wizard with Java, JSON is another animal. Regardless, this blog post explains all you need to get the job done.
What is a Java Object?
A Java object is a combination of data and procedures that work on the available data.
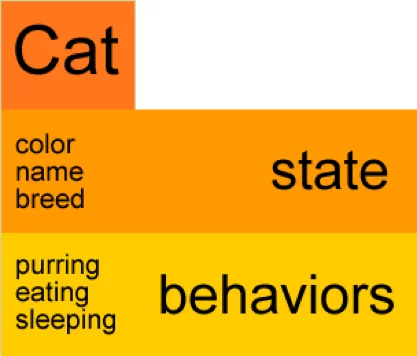
Objects have both states and behaviors. In Java, an object is created using the keyword “new”.
Objects are created from templates known as classes.
An object is an instance of a class.
For example, our “Cat object” has:States – color, name, breed
the state of an object is stored in fields (variables). Behavior – purring, eating, sleeping methods (functions) display the object’s behavior.
What is a JSON String?
- JSON is an acronym for JavaScript Object Notation.
- JSON was designed as a data interchange format and has a syntax that is a subset of JavaScript.
- Context which is surrounded by quotes (single or double), loaded from a text file etc. are called JSON strings.
e.g.
{“id”:1,”name”:”SiAm”,”color”:”Cream”,”eyecolor”:”Blue”,”breed”:”Siamese”} - JSON is interoperable meaning that it’s language/platform independent.
- JSON format is used for serializing and transmitting structured data over a network connection. It is used primarily to transmit data between a server and mobile/web application, serving as an alternative to XML.
Common Uses for Converting Java Obj. to JSON String
The example below demonstrates a client server scenario where the RESTful Web Service accepts data in XML/JSON.
- The RESTful web server app is designed using java:
- enduser doesn’t understand the xml/json but that’s not an issue
- the enduser communicates with a mobile app which might be android
- the enduser communicates with a mobile app which might be php
- the mobile/web app communicates with the RESTful web service via XML/JSON
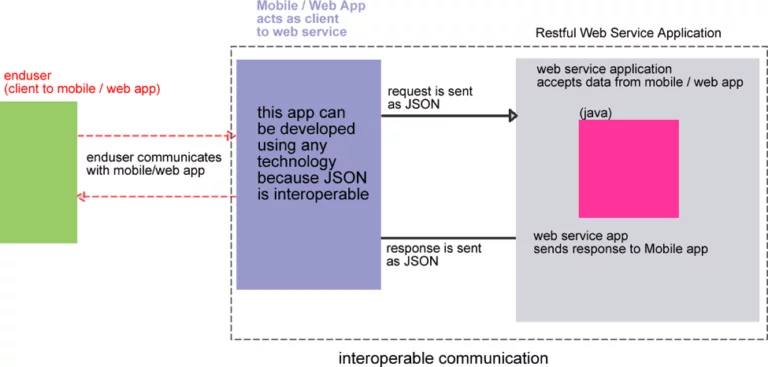
When would you want to convert from Java Obj to JSON string?
In our example diagram above, our RESTful web service was designed using Java.

Since Java objects are only understood by Java applications we need to convert the java object to JSON when creating a web service for the android app. Let’s say the mobile app is a hybrid app where the front end is handled by android view and the data transactions are sent through its own web services using JSON. In this instance we need to send/receive requests from the android app to/from our database using web services/api using JSON data structure.
- JSON is a simple string format data. JSON is readable format. It is very easy to read and infer information from it.
- JSON format is simple to use.
- JSON is quite light-weight compared to other formats like XML etc,.
- JSON format can be easily converted into Java objects in an Object oriented manner.
- JSON is interoperable: program and platform independent.
Java Object to Json String: Tutorial
Step by step examples of how to convert Java Object to JSON string
The most common way to convert Java Object to JSON string is to use an API. The most common APIs for this purpose are Jackson and GSON.
JACKSON API example
This example shows how to use JACKSON API to convert a Java Object into a JSON String.
We can use the ObjectMapper class provided by the Jackson API for our conversion.
- writeValueAsString() is used to convert java obj to JSON
- readValue() is used to convert JSON into java obj
Step 1: Include the JACKSON JAR files into your classpath.
When using MAVEN for dependency management (recommended) you can include the following dependency to download JAR files, any dependency for JACKSON and automatically include it in your project’s classpath.
Add the following dependency to the pom file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <dependencies><dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.8</version></dependency></dependencies> |
Step 2: Use the Jackson API ObjectMapper class to convert Java Object to a JSON string
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();try { String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(cat); System.out.println("ResultingJSONstring = " + json); //System.out.println(json);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) { e.printStackTrace();} |
This example uses the following code:
class useJACKSONapiToConvertJavaOBJtoJSONstring
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; public class useJACKSONapiToConvertJavaOBJtoJSONstring { public static void main(String[] args) { Cat cat = new Cat(); cat.setId(1L); cat.setName("SiAm"); cat.setColor("Cream"); cat.setEyecolor("Blue"); cat.setBreed("Siamese"); ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); try { String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(cat); System.out.println("ResultingJSONstring = " + json); //System.out.println(json); } catch (JsonProcessingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } class Cat |
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | public class Cat { private Long id; private String name; private String color; private String eyecolor; private String breed; public Cat() { public Cat(Long id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; // Getters & Setters @Override public String toString() { return "Cat{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public String getEyecolor() { return eyecolor; public void setEyecolor(String eyecolor) { this.eyecolor = eyecolor; } public String getBreed() { return breed; } public void setBreed(String breed) { this.breed = breed; } } |
Step 3: RUN useJACKSONapitoConvertJavaOBJtoJSONstring
1 | ResultingJSONstring = {"id":1,"name":"SiAm","color":"Cream","eyecolor":"Blue","breed":"Siamese"} |
GSON API example
Find the best examples of Java code snippets using com.google.gson.
The below example shows how to use GSON API to convert a Java Object into a JSON String.
Step 1: Include the GSON JAR files into your classpath
When using MAVEN for dependency management (recommended) you can include the following dependency to download JAR files, any dependency for GSON and automatically include in your project’s classpath as follows:
Add the following dependency to the pom file:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <dependencies><dependency> <groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId> <artifactId>gson</artifactId> <version>2.3.1</version> </dependency></dependencies> |
Step 2: Create class UseGSONapitoConvertJavaOBJtoJASONstring
call the GSON API using: Gson gson = new Gson();
This example uses the following code:
class UseGSONapitoConvertJavaOBJtoJASONstring
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 | import com.google.gson.Gson; public class UseGSONapitoConvertJavaOBJtoJASONstring{ public static void main(String args[]) { CatDetails user = new CatDetails("SiAm", "Siamese", "siam.cat@gmail.com", 9, 2129991234L, "NewCatadonia", true); Gson gson = new Gson(); String json = gson.toJson(user); System.out.println(json); } |
Class CatDetails
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 | /** * Java Program to map a Java object to JSON String using GSON library. */class CatDetails { private String name; private String breed; private String email; private int catlives; private long phone; private String city; private boolean likesMice; public CatDetails(String name, String breed, String email, int catlives, long phone, String city, boolean likesMice) { super(); this.name = name; this.email = email; this.catlives = catlives; this.phone = phone; this.city = city; this.likesMice = likesMice; this.breed = breed;//getters & setterspublic String getName() { return name;}public void setName(String name) { this.name = name;}public String getBreed() { return breed;}public void setBreed(String breed) { this.breed = breed;}public String getEmail() { return email;}public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email;}public int getCatlives() { return catlives;}public void setCatlives(int catlives) { this.catlives = catlives;}public long getPhone() { return phone;}public void setPhone(long phone) { this.phone = phone;}public String getCity() { return city;} public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city;}public boolean isLikesMice() { return likesMice;}public void setLikesMice(boolean likesMice) { this.likesMice = likesMice;}} |
Result:
Step 3:RUN UseGSONapitoConvertJavaOBJtoJASONstring
1 | {"name":"SiAm","breed":"Siamese","email":"siam.cat@gmail.com","catlives":9,"phone":2129991234,"city":"NewCatadonia","likesMice":true} |
Conclusion
Converting a Java Obj to JSON string is simple using JACKSON or GSON API.
In our examples we provided the code to make it easy for you to reproduce in your IDE.
All you need to do is:
- Create a new project (Maven is recommended)
- Include the JAR files into your classpath by adding dependencies to the pom file.
- Create your classes
- Use the JACKSON API: ObjectMapper mapper class
call writeValueAsString(ObjToConvert) method by passing object we want to convert into JSON
or
Use GSON API: class Gson
call toJson(ObjToConvert) method by passing the object we want to convert into JSON;
Run to convert your Java Obj to JSON string.

Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Ilana Brudo, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: How to Convert a Java Object into a JSON String Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |





