Android Launch Modes and Tasks Explained
Android launch modes are a very conceptual topic in Android development and can be easily messed up. There are 4 major launch modes in android that you need to know about:
- Standard
- SingleTop
- SingleInstance
- SingleTask
Launch modes are very frequently asked in android developer interviews and can be tricky if presented with a complex scenario.
Most discussions are around, what happens if ActivityB is launched over ActivityA with launch mode as singleTask. These questions are very common when discussing android launch modes.
To understand launch modes in depth, it’s essential that you understand what is a TASK in android. If you try reading about launch modes without knowing about tasks, then you’ll not be able to understand singleInstance and singleTask launch modes comprehensively.
Hence, I’ll begin this tutorial by first talking about tasks in android and then to the four launch modes in android.
Understanding Tasks in Android
What is a task?
To quote the developer documentation:
A task is a collection of activities that users interact with when performing a certain job.
Think of a Task as a bucket that holds all your activities for your application. A task can have multiple activities and multiple instances of the same activities.
It is based on the STACK data structure and operates as a LIFO (“last in, first out”) structure. Different applications have different tasks and tasks can remain in memory even if application is not in the foreground.
Important to note that an application can have multiple tasks too.
States of a Task
Tasks can be in either Background state or Foreground state. Let’s understand with an example.
Suppose you have an application A with 4 activities and it’s currently in the foreground. If you press the home button, the ENTIRE task will be moved to the background. All the activities of that task will be stopped.
Then you open another application B, and open a couple of activities there. Task for that application is in the foreground now. All of this time, A’s task is still in memory.
When you press home again, B’s task goes to the background and A’s comes to foreground. All the activities of task A are in the correct order as they were. If there’s any text fields, they also preserve their data.
This is how tasks work. This is imperative to understanding android launch modes. They’ll make more sense when you have a clear understanding of tasks.
Android Launch Modes
Standard
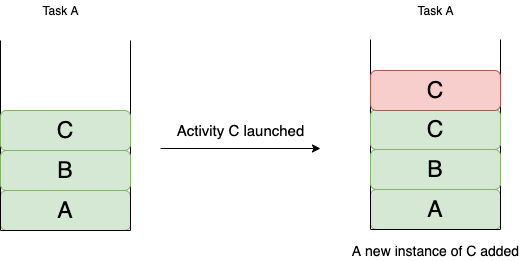
This is the default launch mode. If you don’t specify any launch mode, activity will open with standard launch mode.
This is the simplest of all. It’ll just launch one activity over the other. Even if the activity is already present.
For example:
SingleTop
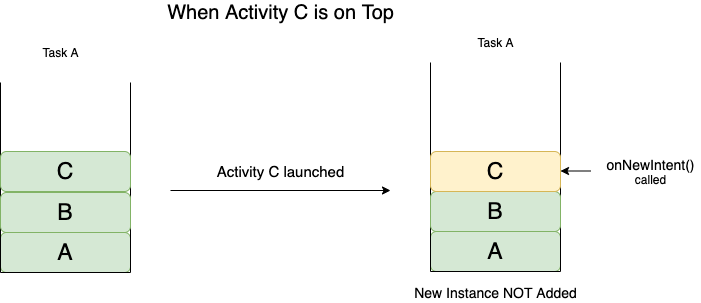
Remember this as: Only a single instance of the activity will remain on top.
In this android launch mode:
- If the Activity is present on the top, then a new instance is NOT created. Instead the onNewIntent() method is invoked.
- If the activity is NOT present on the top, then a new instance is created and added to the top. Just like the standard launch mode.
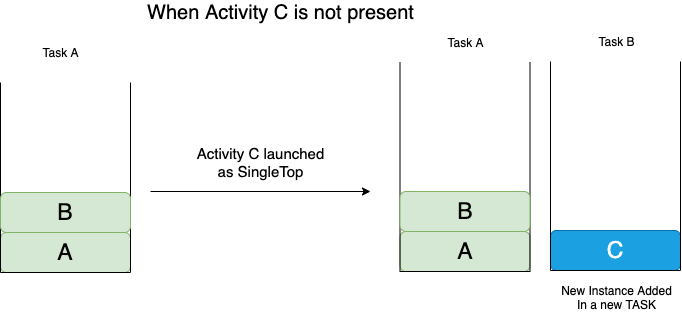
SingleTask
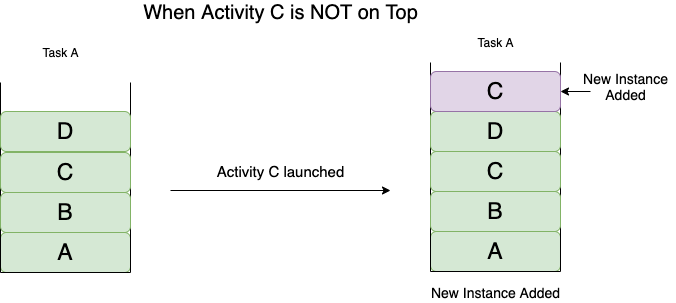
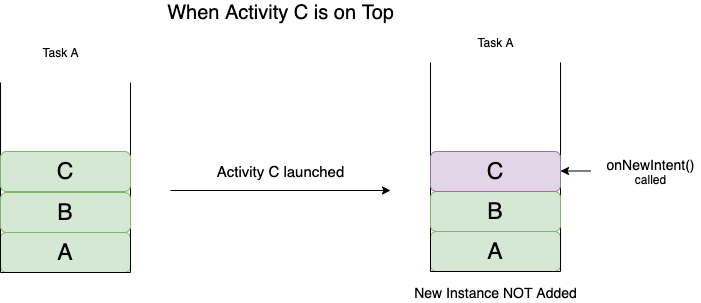
Remember this as: Only a single instance of an activity can survive in a Task.
If an activity has SingleTask launch mode, then a new Task is created when the activity is launched the first time. And this activity instance is placed at the root. Now for the two cases:
In this android launch mode:
- If an Activity is present on top, then a new instance is NOT created. Instead the onNewIntent() method is invoked.
- If an instance of the Activity is already present but NOT ON TOP, it pops all the other activities and invokes the onNewIntent() method.
SingleInstance
Remember this as Single Instance in Single Task
In this android launch mode, just like Single Task a new Task is created and the activity placed at the root. But this new task will only contain that activity instance and nothing else. If a new activity is launched from this, then it’s done in a separate task.
Since only one instance can remain in a task:
- If an instance of the activity exists in a different task, then onNewIntent() method is called for that activity.
- If a new Activity is launched from a singleInstance activity, it’s launched in a separate task.
Some tidbits:
Difference between singleTask and singleInstance:
In singleTask, a new Task is launched and that new task can contain other activities as well.
In singleInstance, a new Task is launched and that cannot contain other activities.
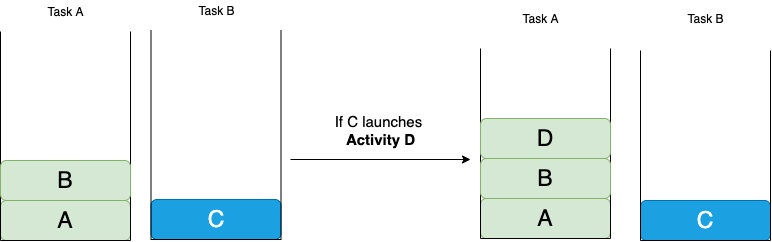
A Nuance:
If a task with activity A declared as singleTask exists in the background, and a foreground activity calls activity A, then the entire task of activity A is placed on top of the activity.
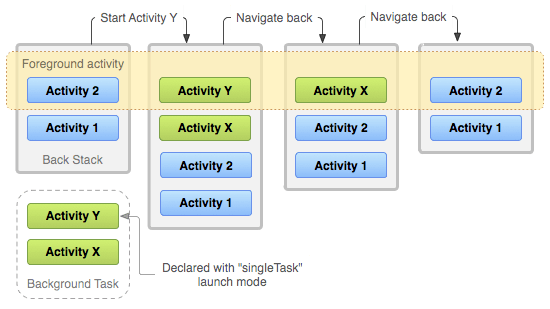
source: https://developer.android.com/guide/components/activities/tasks-and-back-stack
| Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Ayusch Jain, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: Android Launch Modes and Tasks Explained Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |