Project Management Tools: Kanban vs. Scrum Boards
Project management is the practice of planning, organizing, and executing tasks and resources in order to achieve a specific goal or objective within a given timeframe and budget. Effective project management involves a range of skills, including communication, leadership, organization, problem-solving, and time management.
Table Of Contents
1. Basic Aspects Of Project Management
1.1 Key Components Of Project Management
Here are some of the key components of project management:
- Project planning: This involves defining the scope of the project, setting goals and objectives, identifying the tasks and resources needed to complete the project, and creating a project timeline.
- Project organization: This involves assigning roles and responsibilities to team members, developing a project team, and setting up communication channels for collaboration and feedback.
- Project execution: This involves carrying out the project plan, monitoring progress, and making adjustments as needed to ensure that the project stays on track.
- Project monitoring and control: This involves tracking project progress against the project plan, identifying any issues or risks, and taking corrective action to address them.
- Project closure: This involves reviewing the project outcomes, documenting any lessons learned, and formally closing the project.
There are many tools and techniques available for project management, ranging from simple spreadsheets and checklists to specialized project management software that can help automate and streamline project management tasks. Some popular project management tools include Trello, Asana, JIRA, and Microsoft Project. The choice of tool will depend on the specific needs of the project and the preferences of the project manager and team.
1.2 Features of Project Management
Here are some of the key features of project management:
- Project planning: Project planning involves defining the project scope, identifying goals and objectives, creating a project schedule, and determining the resources needed to complete the project. The planning stage sets the foundation for the project and ensures that everyone involved understands the project objectives and what needs to be done to achieve them.
- Task management: Task management involves breaking the project down into smaller, more manageable tasks and assigning them to team members. It also involves setting task priorities and deadlines and monitoring task progress to ensure that the project stays on schedule.
- Resource management: Resource management involves identifying the resources needed to complete the project, such as people, equipment, and materials. It also involves allocating resources to specific tasks and ensuring that resources are used efficiently and effectively throughout the project.
- Team collaboration: Team collaboration is essential for project success. Effective project management involves setting up communication channels and collaboration tools to facilitate team communication and ensure that everyone is working together towards the same goals.
- Risk management: Risk management involves identifying potential project risks and developing strategies to mitigate them. It also involves monitoring project risks throughout the project and taking corrective action as needed to minimize their impact on project outcomes.
- Budget management: Budget management involves tracking project costs and ensuring that the project stays within budget. This includes creating a budget plan, monitoring expenses, and making adjustments as needed to stay on track.
- Project reporting: Project reporting involves providing regular updates on project progress to stakeholders, including project sponsors, team members, and other interested parties. This helps ensure that everyone is informed about project status and can make informed decisions about the project.
There are many project management tools available that offer these and other features, including Trello, Asana, JIRA, and Microsoft Project. The choice of tool will depend on the specific needs of the project and the preferences of the project manager and team.
1.3 Types Of Project Management
There are several different types of project management, each with its own approach and methodology. Here are some of the most common types of project management:
- Traditional project management: Also known as Waterfall project management, this approach involves a linear, sequential process where each stage of the project is completed before moving on to the next. This approach works well for projects with well-defined requirements and predictable outcomes, but can be inflexible and difficult to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Agile project management: Agile project management is a flexible and iterative approach that emphasizes collaboration, customer satisfaction, and the ability to adapt to changing requirements. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, involve breaking the project down into smaller, more manageable components and delivering them in short iterations or sprints.
- Lean project management: Lean project management is focused on delivering value to the customer while minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. This approach emphasizes continuous improvement and focuses on delivering only the features that are most important to the customer.
- Six Sigma project management: Six Sigma is a data-driven approach to project management that emphasizes reducing defects and variability in processes. This approach involves defining, measuring, analyzing, improving, and controlling processes to achieve continuous improvement.
- Critical Chain project management: Critical Chain project management is a variation of traditional project management that focuses on identifying and managing constraints in the project schedule. This approach involves identifying the critical path of the project and focusing resources on completing the most critical tasks.
Each type of project management has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of methodology will depend on the specific needs of the project and the preferences of the project manager and team.
Below we will examine thoroughly the aspects of Kanban and Scrum Boards
2. Kanban Boards Features And Types
Kanban boards are a popular tool for visualizing and managing workflow in project management. A Kanban board typically consists of a physical or digital board with columns representing different stages of the workflow, such as “To Do”, “In Progress”, and “Done”. Cards representing individual tasks or work items are moved between columns as they progress through the workflow.
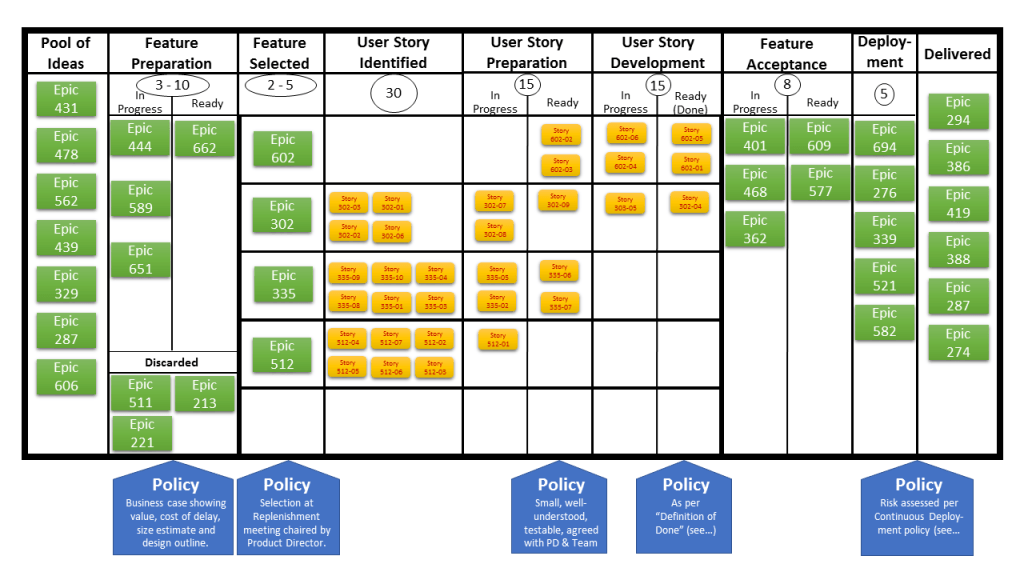
Here are some of the key features and benefits of Kanban boards:
- Visualizing workflow: Kanban boards provide a visual representation of the workflow, making it easy to see the status of each task and the overall progress of the project.
- Limiting work in progress: Kanban boards typically limit the number of tasks that can be in progress at any one time, which can help prevent team members from becoming overwhelmed and improve overall productivity.
- Prioritizing work: Kanban boards make it easy to prioritize work items based on their importance and urgency, helping team members focus on the most important tasks.
- Encouraging collaboration: Kanban boards encourage collaboration and communication between team members, as they can see what others are working on and coordinate their efforts accordingly.
- Continuous improvement: Kanban boards promote continuous improvement by encouraging team members to identify and address bottlenecks in the workflow and make adjustments as needed to improve efficiency and productivity.
There are many Kanban board tools available, ranging from physical whiteboards and sticky notes to digital tools such as Trello, Asana, and JIRA. The choice of tool will depend on the specific needs of the project and the preferences of the project manager and team.
There are several different types of Kanban boards, each with its own unique features and benefits.
Here are some of the most common types of Kanban boards:
- Physical Kanban boards: Physical Kanban boards are physical boards with columns and cards that can be moved around manually. These boards are ideal for teams who prefer a tactile, hands-on approach to project management.
- Digital Kanban boards: Digital Kanban boards are online tools that allow teams to manage their workflow digitally. These boards are often more customizable than physical boards and can include features such as automatic notifications and integrations with other project management tools.
- Personal Kanban boards: Personal Kanban boards are individual boards used by individuals to manage their own workflow. These boards are often used to manage personal tasks and projects and can be a useful tool for increasing productivity and reducing stress.
- Team Kanban boards: Team Kanban boards are used by teams to manage their workflow and collaborate on projects. These boards are often customizable to the specific needs of the team and can include features such as swimlanes and WIP (work in progress) limits.
- Value stream Kanban boards: Value stream Kanban boards are used to map out the entire value stream of a process, from start to finish. These boards can help teams identify areas of waste and inefficiency and make improvements to the overall process.
- Portfolio Kanban boards: Portfolio Kanban boards are used to manage multiple projects or programs within an organization. These boards provide a high-level overview of all projects and can help ensure that resources are allocated effectively.
The type of Kanban board that is most appropriate for a particular project will depend on a variety of factors, including the size of the team, the complexity of the project, and the tools and resources available.
3. Scrum Boards Features And Types
Scrum boards are a visual tool used in agile project management to help teams track and manage their work. A Scrum board typically consists of a physical or digital board divided into columns that represent different stages of the project, such as “To Do”, “In Progress”, and “Done”. Sticky notes or cards are used to represent individual tasks or user stories and are moved between columns as they progress through the workflow.
Here are some of the key features and benefits of Scrum boards:
- Visualizing progress: Scrum boards provide a visual representation of the project, making it easy to see the status of each task and the overall progress of the project.
- Encouraging collaboration: Scrum boards encourage collaboration and communication between team members, as they can see what others are working on and coordinate their efforts accordingly.
- Facilitating Agile methodology: Scrum boards are a core component of the Agile methodology, which emphasizes iterative development and continuous improvement.
- Supporting self-organizing teams: Scrum boards support self-organizing teams by allowing team members to take ownership of their work and collaborate on tasks without being micromanaged.
- Facilitating daily stand-up meetings: Scrum boards are often used during daily stand-up meetings, where team members provide updates on their progress and identify any obstacles or issues that need to be addressed.
There are many Scrum board tools available, ranging from physical whiteboards and sticky notes to digital tools such as JIRA, Trello, and Asana. The choice of tool will depend on the specific needs of the project and the preferences of the project manager and team.
There are several types of Scrum boards that can be used in agile project management.
Here are some of the most common types:
- Physical Scrum boards: Physical Scrum boards are typically whiteboards or bulletin boards with columns and cards that represent tasks or user stories. These boards are popular for small teams who prefer a hands-on approach to project management.
- Digital Scrum boards: Digital Scrum boards are online tools that allow teams to manage their workflow digitally. These boards can be accessed from anywhere and can include features such as automatic notifications and integrations with other project management tools.
- Personal Scrum boards: Personal Scrum boards are used by individuals to manage their own work and prioritize tasks. These boards are often used in combination with team Scrum boards to ensure alignment and coordination.
- Team Scrum boards: Team Scrum boards are used by teams to manage their workflow and collaborate on projects. These boards typically include columns for tasks that are “To Do”, “In Progress”, and “Done” and may include additional columns for specific stages of the project.
- Portfolio Scrum boards: Portfolio Scrum boards are used to manage multiple projects or programs within an organization. These boards provide a high-level overview of all projects and can help ensure that resources are allocated effectively.
- Agile Release Train (ART) Scrum boards: ART Scrum boards are used in large-scale agile projects that involve multiple teams working together. These boards provide a visual representation of the entire project and allow teams to coordinate their efforts and ensure alignment across the organization.
The type of Scrum board that is most appropriate for a particular project will depend on a variety of factors, including the size of the team, the complexity of the project, and the tools and resources available. It is important to choose a Scrum board that aligns with the needs of the project and the preferences of the team.
4. Scrum & Kanban Boards Differences
Kanban and Scrum boards are both visual management tools used in agile project management.
Here are some key differences between Kanban boards and Scrum boards:
- Focus: Kanban boards focus on visualizing and managing flow, whereas Scrum boards focus on sprint planning and progress tracking.
- Work items: Kanban boards allow for flexibility in the type and size of work items that can be included, whereas Scrum boards typically use user stories or tasks that can be completed within a sprint.
- Process: Kanban boards emphasize a continuous flow of work, whereas Scrum boards emphasize iterative development within a sprint.
- Roles: Kanban boards do not have prescribed roles, whereas Scrum boards have specific roles such as Scrum Master and Product Owner.
- Timeboxing: Kanban boards do not use timeboxing, whereas Scrum boards use timeboxed sprints.
- Prioritization: Kanban boards prioritize work items based on their position on the board, whereas Scrum boards prioritize work items based on their importance to the sprint goal.
In summary, Kanban boards and Scrum boards differ in their focus, the type of work items used, their approach to process, roles, timeboxing, and prioritization. The choice between the two types of boards depends on the needs of the project and the preferences of the team. Kanban boards are ideal for teams that prioritize a continuous flow of work, whereas Scrum boards are ideal for teams that need to manage and prioritize work within a timeboxed sprint.
5. Benefits of Using Boards in Project Management
Boards are an important tool in project management as they provide a visual representation of the project’s status and progress. Here are some benefits of using boards in project management:
- Better organization: Boards help to organize tasks and information in a clear and concise manner. By having a visual representation of the project, team members can easily identify what needs to be done and by when.
- Improved communication: Boards improve communication by providing a common understanding of the project’s goals, priorities, and progress. This allows team members to work collaboratively and make decisions more quickly.
- Increased transparency: Boards increase transparency by allowing team members and stakeholders to see the project’s status and progress. This can help to build trust and promote accountability.
- Better time management: Boards help to manage time by providing a clear picture of what tasks are coming up, what tasks are in progress, and what tasks have been completed. This allows team members to prioritize their work and ensure that they are meeting deadlines.
- Improved productivity: Boards can help to improve productivity by providing a clear focus and direction for the team. By having a visual representation of what needs to be done, team members can stay on track and avoid distractions.
- Continuous improvement: Boards can help to facilitate continuous improvement by allowing team members to reflect on their work and identify areas for improvement. This allows the team to learn from their mistakes and make adjustments as necessary.
In summary, boards are an essential tool in project management as they help to improve organization, communication, transparency, time management, productivity, and continuous improvement. By using boards, teams can work more efficiently and effectively, resulting in a higher likelihood of project success.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, boards are an important aspect of project management that can help teams to stay organized, communicate more effectively, and manage their time more efficiently. By providing a visual representation of the project’s status and progress, boards allow team members to work collaboratively and make decisions more quickly. Additionally, boards increase transparency and accountability, which can help to build trust and ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals. Overall, boards are an essential tool for any project manager or team looking to improve their productivity and achieve project success.


