Difference Between Java and JavaScript
1. Introduction
We look at the comparison of Java vs JavaScript languages in this article. JavaScript was developed by Netscape. It was initially a scripting language for the client-side and later used as a language for both client-side and server-side scripting. Java was developed by James Gosling from Sun Microsystems. JavaScript is used in the server in the form of node.js these days. There are many differences between Java and JavaScript related to the way the programs are coded, compiled, and run.
JavaScript was called Mocha first and then LiveScript. Now it is referred to as the current name. Java was called Oak and then Green.
You can also check this tutorial in the following video:
2. Difference Between Java and JavaScript
2.1 Prerequisites
Java 8 is required on the Linux, windows or mac operating system. Eclipse Oxygen can be used for this example. Node.js is bundled with Eclipse installation.
2.2 Download
You can download Java 8 from the Oracle web site . Eclipse Oxygen can be downloaded from the eclipse web site. Node.js can be downloaded from this site.
2.3 Setup
2.3.1 Java Setup
Below is the setup commands required for the Java Environment.
Setup
1 2 3 4 | JAVA_HOME="/desktop/jdk1.8.0_73"export JAVA_HOMEPATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATHexport PATH |
2.4 IDE
2.4.1 Eclipse Oxygen Setup
The ‘eclipse-java-oxygen-2-macosx-cocoa-x86_64.tar’ can be downloaded from the eclipse website. The tar file is opened by double click. The tar file is unzipped by using the archive utility. After unzipping, you will find the eclipse icon in the folder. You can move the eclipse icon from the folder to applications by dragging the icon.
2.5 Launching IDE
2.5.1 Eclipse Java
Eclipse has features related to language support, customization, and extension. You can click on the eclipse icon to launch eclipse. The eclipse screen pops up as shown in the screen shot below:

You can select the workspace from the screen which pops up. The attached image shows how it can be selected.

You can see the eclipse workbench on the screen. The attached screen shot shows the Eclipse project screen.

Java Hello World class prints the greetings. The screenshot below is added to show the class and execution on eclipse.

You can create a JavaScript project from the menu and name the project as shown in the screen shot below:
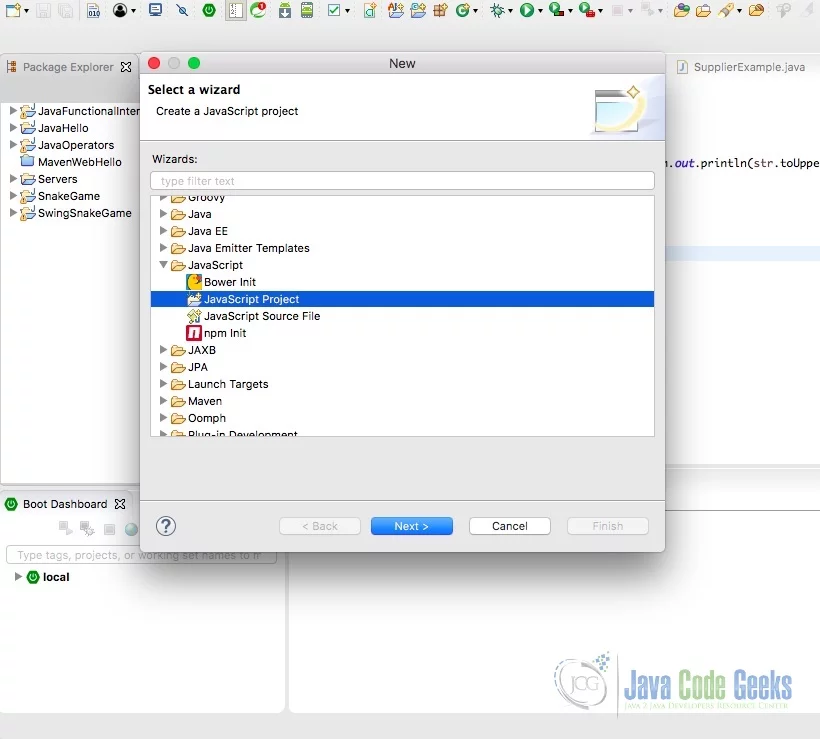
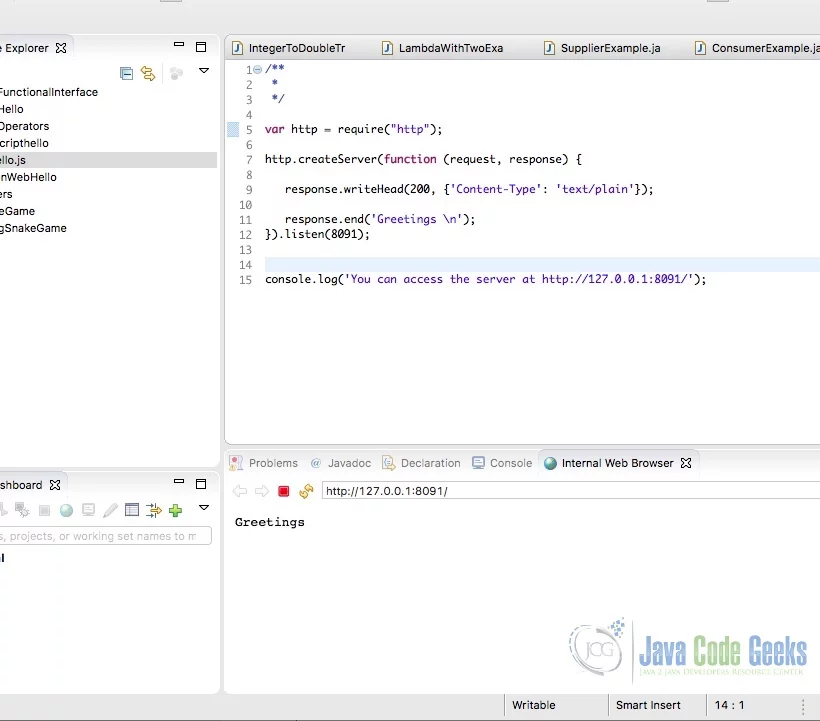
JavaScript (Node.js) hello program is executed in the IDE. The output “Greetings” is shown in the screenshot below.
2.6 Memory Management
Java language has features related to memory management and it is a memory-safe language. Garbage collection is a feature that helps in collecting the resources which are free and released. Java developers cannot go beyond the allocated memory. In java, when the memory is consumed beyond the allocation, it throws an error. JavaScript requires lesser memory compared to java. This is used extensively for client-side scripting in web pages.
2.7 Exceptional Handling
In Java, exception handling is possible by using try, catch and finally blocks.
Java Exception Handling
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class ExceptionExample{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ try{ int result=36/0; System.out.println(" the result is "+result); } catch(ArithmeticException exception) { System.out.println(exception); throw new Exception("division by zero"); } finally { System.out.println("finally block is executed at the end");} System.out.println("code below is used for next steps"); } } |
JavaScript has try, catch, throw, and finally blocks to handle exception handling.
Javascript Exception Handling
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | console.log("entering try-catch statement");try { console.log("entering try block"); throw "thrown message"; console.log("this message is never seen");}catch (e) { console.log("entering catch block"); console.log(e); console.log("leaving catch block");}finally { console.log("entering and leaving the finally block");}console.log("leaving try-catch statement"); |
2.8 Multiple Inheritance
Let us take an example to see how it is handled in Java and JavaScript. A truck is a vehicle and a machine.

Java does not support multiple inheritance. Each class can extend only on one class but is able to implement more than one interface. The sample code shows below Truck class implementing interfaces Machine and VehicleInterfaces
Multiple Inheritance Example
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | interface Machine{ int distanceTravelled=100; public int getDistance();}interface Vehicle{ int velocity=50; public int getVelocity();}public class Truck implements Machine, Vehicle{ int time; int velocity; int distanceTravelled; public Truck(int velocity, int time) { this.velocity = velocity; this.time = time; } public int getDistance() { distanceTravelled= velocity*time; System.out.println("Total Distance is : "+distanceTravelled); return distanceTravelled; } public int getVelocity() { int velocity=distanceTravelled/time; System.out.println("Velocity is : "+ velocity); return velocity; } public static void main(String args[]) { Truck truck = new Truck(50,2); truck.getDistance(); truck.getVelocity(); }} |
JavaScript supports multiple inheritance using inheritsMultipleObjects function. The below example shows how Truck can inherit the functions getDistance and getVelocity from Vehicle and Machine respectively.
Multiple Inheritance – Javascript
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | function inheritsMultipleObjects(baseObject, superObjects) { return new Proxy( baseObject, { get(target, key, rec) { if (Reflect.ownKeys(target).includes(key)) { return Reflect.get(target, key); } const parent = superObjects.find( _parent => Reflect.has(_parent, key) ); if (parent !== undefined) { return Reflect.get(parent, key); } return undefined; }, has(target, key) { if (Reflect.ownKeys(target).includes(key)) { return true; } const parentHasKey = superObjects.some( _parent => Reflect.has(_parent, key) ); if (parentHasKey) { return true; } return false; } } );}class Vehicle { getDistance() { return 100; }}class Machine { getVelocity() { return 50; }}class Truck {}const _truck = new Truck();const truck = inheritsMultipleObjects( _truck, [Truck.prototype,Vehicle.prototype, Machine.prototype]);console.log(truck.getDistance()); console.log(truck.getVelocity()); console.log(truck.constructor); |
2.9 Threads
Java has built-in classes to create threads. To create a new thread, a class has to extend a Thread class and the run method has to be overridden.
Thread Example
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 | public class NewThread extends Thread{ public void run() { System.out.println("Thread running now"); } public static void main(String args[]) { NewThread newThread =new NewThread(); newThread.start(); } } |
Java provides another way to create Threads. A class that implements Runnable can be instantiated and passed as a parameter to the Thread class. Sample code is provided below:
Thread Object – Runnable
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 | public class ThreadObject implements Runnable{ public void run() { System.out.println("ThreadObject running"); } public static void main(String args[]){ ThreadObject threadObject =new ThreadObject(); Thread thread =new Thread(threadObject); thread.start(); } } |
JavaScript has event-based mechanisms to handle concurrency. Node.js is a single-threaded language. It uses more than one threads to execute code asynchronously in the background. Let us look at the forking the thread example in the code below:
Forking the thread
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 | const { fork } = require('child_process');var express = require('express');var app = express();app.get('/endpoint', (request, response) => { const process = fork('./mail.js'); const mail_messages = request.body.emails; process.send({ mail_messages }); process.on('sendmail', (message) => { log.info(` mail count ${message.counter}`); }); return response.json({ status: true, sent: true });}); |
The code below shows how sendMultiplemails is executed asynchronously.
Sending the mail
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 | async function sendMultipleMails(mails) { let sendMails = 0; // code for sending multiple mails return sendMails;}process.on('sendmail', async (message) => { const countOfMailsSent = await sendMultipleMails(message.mails); process.send({ counter: countOfMailsSent });}); |
2.10 Portability
Java language is interpreted by the Java interpreter on the computer independent of the operating system. Java programs are executed as byte code on the java virtual machine. The java code is in the programs with extension .java.

JavaScript is used in HTML pages for client-side scripting which is executed on the browser. Node.js based server-side scripts are executed by the Version 8 (ECMAScript) JavaScript engine on the specific operating system. The code is written in files with extension .js.
2.11 Types
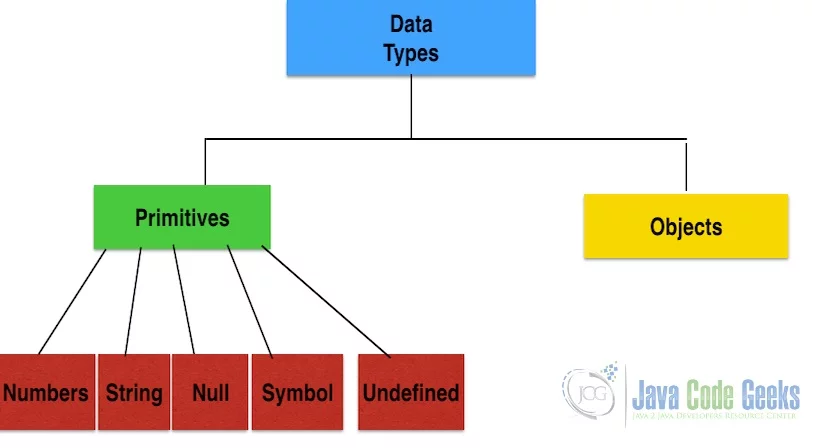
Java is a statically typed language. Java language has primitive and object types. Java has features related to autoboxing which converts the types automatically. The java.lang.Object class is the base class for all the classes and Java follows the single root chain of command.

JavaScript is a dynamically typed language. During the compilation time, variables are declared using var keyword. The types are handled dynamically when checked for equality or any other operators.
2.12 Libraries
Java packages help in packaging classes. Package scope is another feature in Java language. Java archives help in grouping the package of classes for execution and installation purposes.

JavaScript modules and packages consist of JavaScript files in node.js and client-side web archives.
2.13 Runtime Errors
In java, runtime errors are presented by the compiler and the interpreter.

JavaScript is a dynamically typed language and hence can handle any type of data. Null pointer exceptions do not happen in JavaScript. Runtime errors happen when the code is run using the runtime (node.js) or in the browser.
2.14 Documentation
Java has a feature to support comments which can be used for documentation generator. JavaScript also has support for comments which can be used for documentation generation.
2.15 Mobile & Web & Desktop
Java language can be used for mobile, web and desktop application development. Java is supported by Android. JavaScript is used to build HTML5 (web) and hybrid mobile apps in Android, IOS and other mobile operating systems.
2.16 Programming Paradigm
Java is an object-oriented, class and concurrent programming language. Java is currently supporting functional programming features from version 8. JavaScript is a multi-paradigm language supporting object-oriented, procedural and functional paradigms.
3. Conclusion
Overall, Java has great benefits over JavaScript. The comparison table below captures the differences between Java and JavaScript.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Java | JavaScript |
| Memory Management | Garbage collection is a feature in Java. Pointers are not there in Java. Java programs consume more memory | JavaScript requires less memory. It is extensively used in web pages |
| Inheritance | Interfaces can be used for multiple inheritance. Single Inheritance is supported in Java. | JavaScript supports multiple inheritance using inheritsMultipleObjects function |
| Threads | Java has class Thread and interface Runnable to use threads. | JavaScript (Node.js) is a single-threaded language that forks a thread to run multiple threads asynchronously. |
| Portability | Java byte code is platform dependent. | JavaScript is platform-independent. The run-time (node runtime) is platform dependent. |
| Access Control | Encapsulation helps in access control of the class variables and properties in java. | JavaScript has object properties to provide access control of the variables. |
| Types | A single root chain of command pattern is used in Java. | JavaScript is a weakly typed language. |
| Libraries | Java archives are used for building java libraries. | JavaScript (Node.js) has modules and packages. |
| Runtime error | Runtime errors are detected in compilation and execution stages in Java | JavaScript run-time errors are detected during the execution stages. |
| Performance | Java performance is slower compared to JavaScript. | JavaScript performance is faster compared to java as interpreters run the JavaScript code themselves. |
4. Download the Source Code
You can download the full source code of this example here: Difference Between Java and JavaScript



