Spring Boot Actuator: custom endpoint with MVC layer on top of it
Spring Boot Actuator endpoints allow you to monitor and interact with your application. Spring Boot includes a number of built-in endpoints and you can also add your own.
Adding custom endpoints is as easy as creating a class that extends from org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.AbstractEndpoint. But Spring Boot Actuator offers also possibility to decorate endpoints with MVC layer.
Endpoints endpoint
There are many built-in endpoints, but one there is missing is the endpoint to expose all endpoints. By default endpoints are exposed via HTTP where ID of an endpoint is mapped to a URL. In the below example, the new endpoint with ID endpoints is created and its invoke method returns all available endpoints:
@Component
public class EndpointsEndpoint extends AbstractEndpoint<List<Endpoint>> {
private List<Endpoint> endpoints;
@Autowired
public EndpointsEndpoint(List<Endpoint> endpoints) {
super("endpoints");
this.endpoints = endpoints;
}
@Override
public List<Endpoint> invoke() {
return endpoints;
}
}@Component annotation adds endpoint to the list of existing endpoints. The /endpoints URL will now expose all endpoints with id, enabled and sensitive properties:
[
{
"id": "trace",
"sensitive": true,
"enabled": true
},
{
"id": "configprops",
"sensitive": true,
"enabled": true
}
]New endpoint will be also registered with JMX server as MBean: [org.springframework.boot:type=Endpoint,name=endpointsEndpoint]
MVC Endpoint
Spring Boot Actuator offers an additional feature which is a strategy for the MVC layer on top of an Endpoint through org.springframework.boot.actuate.endpoint.mvc.MvcEndpoint interfaces. The MvcEndpoint can use @RequestMapping and other Spring MVC features.
Please note that EndpointsEndpoint returns all available endpoints. But it would be nice if user could filter endpoints by its enabled and sensitive properties.
In order to do so a new MvcEndpoint must be created with a valid @RequestMapping method. Please note that using @Controller and @RequestMapping on the class level is not allowed, therefore @Component was used to make the endpoint available:
@Component
public class EndpointsMvcEndpoint extends EndpointMvcAdapter {
private final EndpointsEndpoint delegate;
@Autowired
public EndpointsMvcEndpoint(EndpointsEndpoint delegate) {
super(delegate);
this.delegate = delegate;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/filter", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Set<Endpoint> filter(@RequestParam(required = false) Boolean enabled,
@RequestParam(required = false) Boolean sensitive) {
}
}The new method will be available under /endpoints/filter URL. The implementation of this method is simple: it gets optional enabled and sensitive parameters and filters the delegate’s invoke method result:
@RequestMapping(value = "/filter", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Set<Endpoint> filter(@RequestParam(required = false) Boolean enabled,
@RequestParam(required = false) Boolean sensitive) {
Predicate<Endpoint> isEnabled =
endpoint -> matches(endpoint::isEnabled, ofNullable(enabled));
Predicate<Endpoint> isSensitive =
endpoint -> matches(endpoint::isSensitive, ofNullable(sensitive));
return this.delegate.invoke().stream()
.filter(isEnabled.and(isSensitive))
.collect(toSet());
}
private <T> boolean matches(Supplier<T> supplier, Optional<T> value) {
return !value.isPresent() || supplier.get().equals(value.get());
}Usage examples:
- All enabled endpoints:
/endpoints/filter?enabled=true - All sensitive endpoints:
/endpoints/filter?sensitive=true - All enabled and sensitive endpoints:
/endpoints/filter?enabled=true&sensitive=true
Make endpoints discoverable
EndpointsMvcEndpoint utilizes MVC capabilities, but still returns plain endpoint objects. In case Spring HATEOAS is in the classpath the filter method could be extended to return org.springframework.hateoas.Resource with links to endpoints:
class EndpointResource extends ResourceSupport {
private final String managementContextPath;
private final Endpoint endpoint;
EndpointResource(String managementContextPath, Endpoint endpoint) {
this.managementContextPath = managementContextPath;
this.endpoint = endpoint;
if (endpoint.isEnabled()) {
UriComponentsBuilder path = fromCurrentServletMapping()
.path(this.managementContextPath)
.pathSegment(endpoint.getId());
this.add(new Link(path.build().toUriString(), endpoint.getId()));
}
}
public Endpoint getEndpoint() {
return endpoint;
}
}The EndpointResource will contain a link to each enabled endpoint. Note, that the constructor takes a managamentContextPath variable. This variable contains a Spring Boot Actuator management.contextPath property value. Used to set a prefix for management endpoint.
The changes required in EndpointsMvcEndpoint class:
@Component
public class EndpointsMvcEndpoint extends EndpointMvcAdapter {
@Value("${management.context-path:/}") // default to '/'
private String managementContextPath;
@RequestMapping(value = "/filter", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Set<Endpoint> filter(@RequestParam(required = false) Boolean enabled,
@RequestParam(required = false) Boolean sensitive) {
// predicates declarations
return this.delegate.invoke().stream()
.filter(isEnabled.and(isSensitive))
.map(e -> new EndpointResource(managementContextPath, e))
.collect(toSet());
}
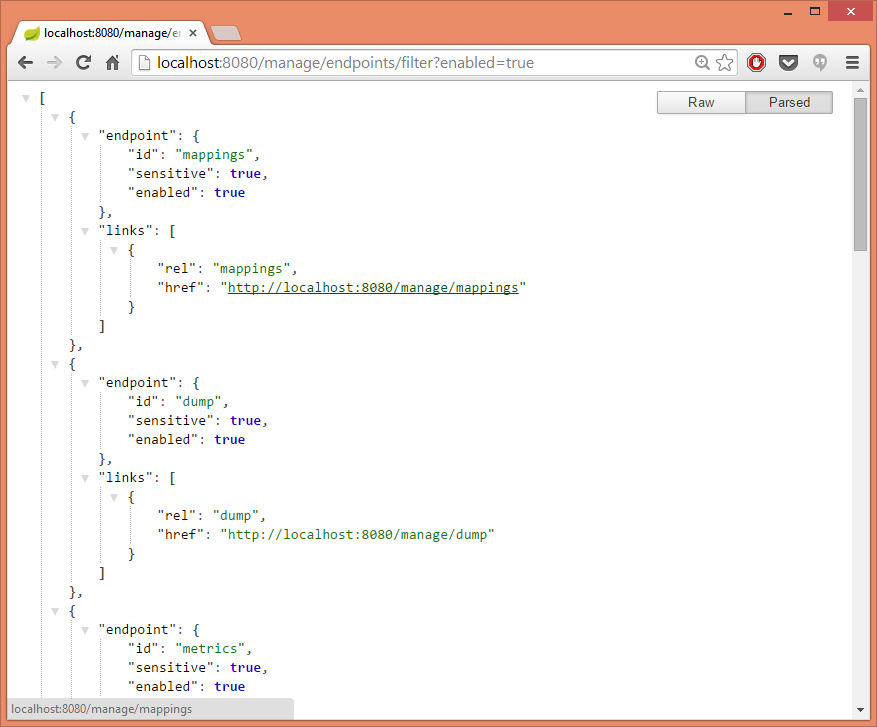
}The result in my Chrome browser with JSON Formatter installed:
But why not returning the resource directly from EndpointsEnpoint? In EndpointResource a UriComponentsBuilder that extracts information from an HttpServletRequest was used which will throw an exception while calling to MBean’s getData operation (unless JMX is not desired).
Manage endpoint state
Endpoints can be used not only for monitoring, but also for management. There is already built-in ShutdownEndpoint (disabled by default) that allows to shutdown the ApplicationContext. In the below (hypothetical) example, user can change state of selected endpoint:
@RequestMapping(value = "/{endpointId}/state")
@ResponseBody
public EndpointResource enable(@PathVariable String endpointId) {
Optional<Endpoint> endpointOptional = this.delegate.invoke().stream()
.filter(e -> e.getId().equals(endpointId))
.findFirst();
if (!endpointOptional.isPresent()) {
throw new RuntimeException("Endpoint not found: " + endpointId);
}
Endpoint endpoint = endpointOptional.get();
((AbstractEndpoint) endpoint).setEnabled(!endpoint.isEnabled());
return new EndpointResource(managementContextPath, endpoint);
}While calling a disabled endpoint user should receive the following response:
{
"message": "This endpoint is disabled"
}Going further
The next step could be adding a user interface for custom (or existing) endpoints, but it is not in scope of this article. If you are interested you may have a look at Spring Boot Admin that is a simple admin interface for Spring Boot applications.
Summary
Spring Boot Actuator provides all of Spring Boot’s production-ready features with a number of built-in endpoints. With minimal effort custom endpoints can be added to extend monitoring and management capabilities of the application.
References
| Reference: | Spring Boot Actuator: custom endpoint with MVC layer on top of it from our JCG partner Rafal Borowiec at the Codeleak.pl blog. |







How is List getting autowired while constructing EndpointsEndpoint object.