Read property files with PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
1. Introduction
Usually when we are concerned with multiple servers where the application is deployed before going into production, we can configure the environment-specific parameters in an external property file. It might be the database details, which is different for test server and the production server. So it’s better we we choose to keep the database configuration file in an external property file. Similarly, we can choose to keep LDAP server details in an external property file. With property files in place, we don’t need to touch the configuration XML files, where the property file values can be directly picked up as ${name}.
All we need to do is to update the property file accordingly at every deployment, without even touching the Spring configuration context files.
In this tutorial, we will see how we can make use of PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer to read external property file values and access them from bean configuration in Spring.
2. Implementation
For a simple demo, let’s create a property file user.properties at some external location with the following content:
name=ramesh
With that in place, lets make sure we have the application context file content as:
applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location">
<value>file:/E:\/user.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.jcombat.bean.HelloWorld">
<property name="name" value="${name}" />
</bean>
</beans>Note the highlighted section in the above snippet.
We have the main class below, which we will try to run.
MainApp.java
package com.jcombat.client;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.jcombat.bean.HelloWorld;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"applicationContext.xml");
HelloWorld hellWorld = (HelloWorld) context.getBean("helloWorld");
hellWorld.sayHello();
((ConfigurableApplicationContext)context).close();
}
}3. Running the application
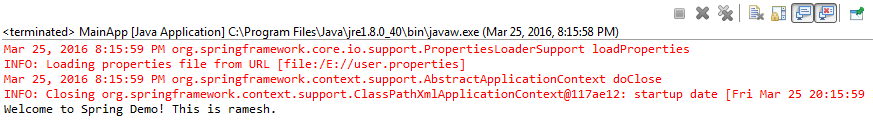
Running the above as java application displays as:
4. Download the source code
| Reference: | Read property files with PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer from our JCG partner Abhimanyu Prasad at the jCombat blog. |