How to Find K Missing Numbers in Integer Array With Duplicates in Java?
It’s been a long time since I have discussed any coding or algorithm interview questions, so I thought to revisit one of the most popular array based coding problem of finding missing numbers in given array. You might have heard or seen this problem before on your programming job interview but there are a lot of different versions of increasing difficulty levels which interviewer normally use to confuse candidate and further test their ability to adapt to frequent changes. In the past I have demonstrated how to find the missing number in a sorted array as well on the unsorted integer array in Java using BitSet (see here), but, with just one missing number and without any duplicates.
That makes the problem somewhat easy but what do you do if interviewer tells you that array contains duplicates and more than one numbers are missing? Well, that’s what we’ll discuss in this article, but before that let’s get the problem statement correctly.
1. Problem Statement:
You have given an integer array of size N. Array contains numbers from 1 to N-1 but a couple of numbers are missing in an array which also contains duplicates. Write a Java program to print the missing number from the sequence.
For example, if given array is
{1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 5, 7, 9, 9, 9} then it has length
10 and contains a number from 1 to 9. In this case, missing numbers are 4, 6, and 8.
2. Solution:
When you see the question is to find missing number in array, you might think about our earlier solution of calculating sum of all the numbers and deducting it from expected sum to find the missing number, but unfortunately that will not work in this situation because more than one number is missing as well it contains duplicates.
In this case, we need to use a different approach, something like a roll-call you would have seen in your school.
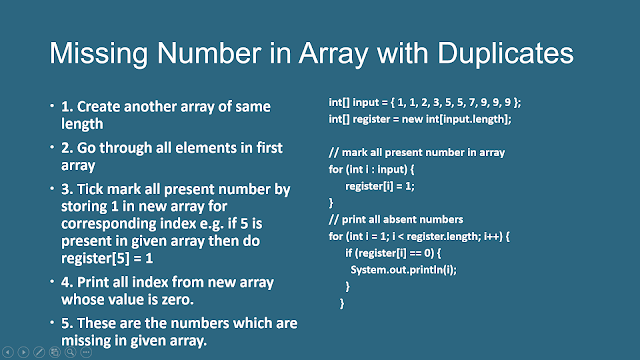
The teacher has a register with names of all students, he goes through the list and mark absences on red. We can use the same approach to find all the missing numbers in the list.
We can use an array as register and it’s index as names of the numbers. We loop through the given array and tick marking all the numbers which are present by storing one of their respective indices. For example, if the first number in given array is 5 (since the array is not sorted) then we store 1 on index 5 e.g. register[5] = 1
Once we have gone through all the numbers is given, we can go through our register array and print all the indices where the value is zero. These are absentees or missing numbers.
This solution is also safe from duplicates because if a number comes once or twice we just store 1 on the respective index.
3. Code:
Now that we know how to solve this problem of missing numbers in unsorted integer array with duplicates, it’s time to turn this solution into a code and working Java program.
/*
* Java Program to find missing numbers in an integer
* array with duplicates. Array may contains more
* than one duplicates.
*
* input: {1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 5, 7, 9, 9, 9};
* output: 4, 6, 8
*/
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// given input
int[] input = { 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 5, 7, 9, 9, 9 };
// let's create another array with same length
// by default all index will contain zero
// default value for int variable
int[] register = new int[input.length];
// now let's iterate over given array to
// mark all present numbers in our register
// array
for (int i : input) {
register[i] = 1;
}
// now, let's print all the absentees
System.out.println("missing numbers in given array");
for (int i = 1; i < register.length; i++) {
if (register[i] == 0) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}Output missing numbers in given array 4 6 8
This is the simplest Java program to solve this problem. You can see that we have hardcoded the input array but you can also modify the program to get input from the user by using Scanner class as shown in this example.
The code is exactly same as a solution, we created another array by copying length from original array and used it mark numbers which are present.
Since array indices are also integer and they are in the range of input values we can leverage them to use both as data and metadata. Had the array contains a number which is not in the range of 1 to N-1 then we couldn’t have used an array.
Here is the summary of algorithm and code in a slide for better understanding:
4. Analysis
Now, the time is to analyze our solution to find the CPU and Memory complexity using Big O notation. If you look at the code then you will find that we are creating another array with the same size which means it has memory or space complexity of O(n).
This means if the array is too big i.e. contains all the numbers in the integer range then we would a lot more memory which may not be available and our program could throw OutOfMemoryError in Java. This is even more possible because array needs a contiguous chunk of memory.
So, if we can remove the additional array which is not really holding anything and find a way to just store missing number which is quite less than the all the number that we can improve this solution, something for you guys to think.
For time complexity, you can see that we iterate through the whole array to mark all present number and then iterate again to another array of the same length to find absentees. This means time complexity of this solution is O(n) + O(n) or O(2N) which is in Big O Notation still O(n).
We can further improve this solution if we find a way to print absentees as we iterate through the given array. Again, something to think of you guys.
That’s all about this classic problem of finding missing numbers in given integer array. In this part, we have found a solution for finding multiple missing numbers in the unsorted array with duplicates. The time and space complexity of our solution is O(n).
| Published on Java Code Geeks with permission by Javin Paul, partner at our JCG program. See the original article here: How to Find K Missing Numbers in Integer Array With Duplicates in Java? Opinions expressed by Java Code Geeks contributors are their own. |



The same thing can be accomplished using a BitSet object and setting bits based on integer values of the input array, instead of using the array to register the missing integers.
System.out.println(“missing numbers in given array”);
for(int j=1;j<arr.length;j++){
if(Arrays.binarySearch(arr, j) < 0){
System.out.println(j);
}
}